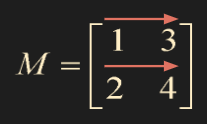Numpy & Scipy - 1.3 Basic Manipulation of Matrices (1)
Numpy & Scipy - 1.3 Basic Manipulation of Matrices (1)
Numpy & Scipy 시리즈 (3 / 9)
- Numpy & Scipy - 1.1 Notation of Matrix and Vector, Matrix Input and Output
- Numpy & Scipy - 1.2 Convenient Functions of Matrix
- Numpy & Scipy - 1.3 Basic Manipulation of Matrices (1)
- Numpy & Scipy - 1.4 Basic Manipulation of Matrices (2)
- Numpy & Scipy - 1.5 Basic Manipulation of Matrices (3)
- Numpy & Scipy - 1.6 The Solution of Matrix Equation (General Matrices)
- Numpy & Scipy - 1.7 The Solution of Band Matrix
- Numpy & Scipy - 1.8 The Solution of Toeplitz Matrix and Circulant Matrix And How to Solve AX=B
- Numpy & Scipy - 1.9 Calculate Eigenvector and Eigenvalue of Matrix
copy (deep copy)
- np.copy : deep copy, 새로운 메모리 공간을 참조하여 할당
reshape (swallow copy)
- np.reshape(matrix, number 또는 shape) : 입력한 matrix 를 원하는 1D vector, 2D matrix 형태로 바꿔서 swallow copy 를 진행한다.
- 여기서 shape 는 tuple 형태의 자료형이다. (2,3) 이면 2x3 matrix
- number 즉 숫자 하나만 입력하면 (3,) 1d vector 임
[1, 2.5, 3, -1, -2, -1.5] [[1, 2.5] [3, -1] [-2, -1.5]]
tril / triu
- np.tril(matrix, band_id) : band_id 를 포함하여 lower 부분들을 deep copy 한다. lower triangular matrix
- 여기서 band_id 는 default parameter 로 생략 가능
1
2
3
4
5
a = np.array([[1,2,3], [4,5,6], [7,8,9]], dtype=np.float64)
b = np.tril(a)
prt(b, "%0.2f", delimiter=" , ")
1
2
3
1.00 , 0.00 , 0.00
4.00 , 5.00 , 0.00
7.00 , 8.00 , 9.00
- np.triu(matrix, band_id) : band_id 를 포함하여 upper 부분을 deep copy. upper triangular matrix
1
2
3
4
5
a = np.array([[1,2,3], [4,5,6], [7,8,9]], dtype=np.float64)
b = np.triu(a)
prt(b, "%0.2f", delimiter=" , ")
1
2
3
1.00 , 2.00 , 3.00
0.00 , 5.00 , 6.00
0.00 , 0.00 , 9.00
diag
- np.diag(matrix, k=band_id) : 특정 band 를 뽑아내어 1D array (vector) 로 만들어 swallow copy 하는 함수
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
a = np.array([[1,2,3], [4,5,6], [7,8,9]], dtype=np.float64)
b = np.diag(a, k=1)
prt(b, "%0.2f", delimiter=" , ")
b[0] = 0.0 # readonly 이기 때문에 에러 발생
1
2.00 , 6.00
입력에 따라 기능이 달라지는 np.diag
- np.diag(matrix, k=band_id) 에서 matrix 에 1D array 를 입력하면 square matrix 를 deep copy 하여 반환 한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
c = np.array([1,2,3,4] , dtype=np.float64) # 1차원 배열을 입력했을때
d = np.diag(c, k=-1) # deep copy 이다.
c[0] = 0.0
prt(d, "%0.2f", delimiter=" , ")
1
2
3
4
5
0.00 , 0.00 , 0.00 , 0.00 , 0.00
1.00 , 0.00 , 0.00 , 0.00 , 0.00
0.00 , 2.00 , 0.00 , 0.00 , 0.00
0.00 , 0.00 , 3.00 , 0.00 , 0.00
0.00 , 0.00 , 0.00 , 4.00 , 0.00
diagflat
- np.diagflat(M, k=band_id) : 항상 square matrix 를 deep copy 하여 만들어준다.
- 주의할점은 여기서 입력되는 M을 1D array 화 시킨 뒤에 square matrix를 생성한다.
- 1d array -> np.diag 와 비슷, 2d array -> 1d 화 한뒤에 square matrix 생성
1
2
3
4
5
M = np.array([[1,3],[2,4]], dtype=np.float64)
e = np.diagflat(M, k = 0)
prt(e, "%0.2f", delimiter=" , ")
1
2
3
4
1.00 , 0.00 , 0.00 , 0.00
0.00 , 3.00 , 0.00 , 0.00
0.00 , 0.00 , 2.00 , 0.00
0.00 , 0.00 , 0.00 , 4.00
trace
- np.trace : diagonal entry 혹은 band entry 들을 더한 값을 반환한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
T = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], dtype=np.float64)
val = np.trace(T)
print(val)
val = np.trace(T, offset=-1) # k 가 아니라 offset 임
print(val)
1
2
3
15
12
flatten method / ravel
- flatten : 행렬 A 를 1D array 화 하여 deep copy 하여 반환한다.
1
2
3
4
5
T = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], dtype=np.float64)
flat = T.flatten()
prt(flat, "%0.2f", delimiter=" , ")
1
1.00 , 2.00 , 3.00 , 4.00 , 5.00 , 6.00 , 7.00 , 8.00 , 9.00
- np.ravel : 행렬 A 를 1D array 화 하여 swallow copy 하여 반환
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
T = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], dtype=np.float64)
rav = np.ravel(T)
T[0,0] = 0.0
prt(rav, "%0.2f", delimiter=" , ")
1
0.00 , 2.00 , 3.00 , 4.00 , 5.00 , 6.00 , 7.00 , 8.00 , 9.00
이 기사는 저작권자의 CC BY 4.0 라이센스를 따릅니다.