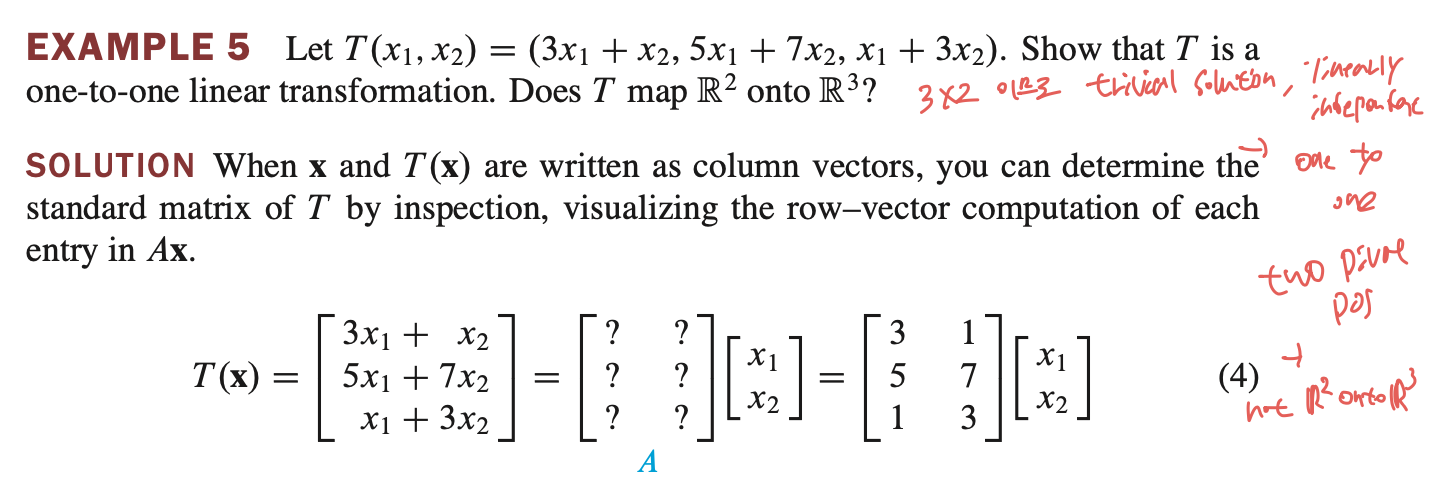
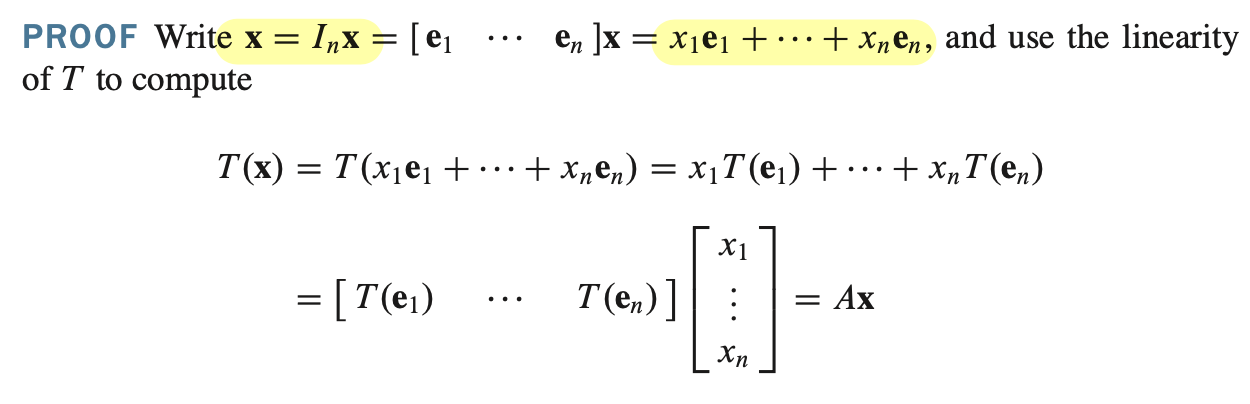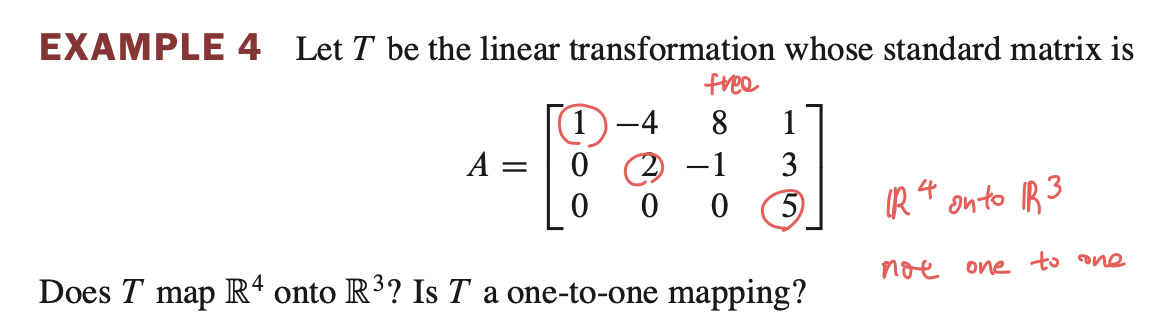Linear Algebra - 1.8 The Matrix of a Linear Transformation
- Linear Algebra - 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations
- Linear Algebra - 1.2 Row Reduction and Echelon Forms
- Linear Algebra - 1.3 Vector Equations
- Linear Algebra - 1.4 The Matrix Equation Ax=b
- Linear Algebra - 1.5 Solution Sets of Linear Systems
- Linear Algebra - 1.6 Linear Independence and Linear Dependence
- Linear Algebra - 1.7 Introduction to Linear Transformation
- Linear Algebra - 1.8 The Matrix of a Linear Transformation
- Linear Algebra - 2.1 Matrix Operations
- Linear Algebra - 2.2 The Inverse of Matrix
- Linear Algebra - 2.3 Characterizations of Invertible Matrices of
- Linear Algebra - 2.4 Partitioned Matrices
- Linear Algebra - 2.5 Matrix Factorizations, LU Decomposition
- Linear Algebra - 2.6 Subspaces of $\mathbb{R}^n$
- Linear Algebra - 2.7 Dimension and Rank
- Linear Algebra - 3.1 Introduction to Determinants
- Linear Algebra - 3.2 Properties of Determinants
- Linear Algebra - 3.3 Cramer's Rule, Volume, And Linear Transformations
- Linear Algebra - 4.1 Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues
- Linear Algebra - 4.2 The Characteristic Equation
- Linear Algebra - 4.3 Diagonalization
- Linear Algebra - 4.4 Eigenvectors And Linear Transformations
- Linear Algebra - 4.5 Complex Eigenvalues
- Linear Algebra - 5.1 Inner Product And Orthogonality
- Linear Algebra - 5.2 Orthogonal Sets
- Linear Algebra - 5.3 Orthogonal Projections
- Linear Algebra - 5.4 The Gram-Schmidt Process (그람 슈미츠 과정)
- Linear Algebra - 5.5 Least-Square Problems
- Linear Algebra - 6.1 Diagonalization of Symmetric Matrices
- Linear Algebra - 6.2 Quadratic Forms
- Linear Algebra - 6.3 Constrained Optimization
- Linear Algebra - 6.4 SVD, The Singular Value Decomposition
- Linear Algebra - 6.5 Reduced SVD, Pseudoinverse, Matrix Classification, Inverse Algorithm
용어 정리
- Matrix Transformation (행렬 변환)
- Standard Matrix (표준 행렬)
- Linear Transformation (선형 변환)
How to determine a matrix transformation - 행렬 변환 결정 방법
- $ \mathbf{A}\mathbf{x} = \mathbf{T}(\mathbf{x}) $ 에서 $ \mathbf{A} $ 를 모를 때 $ \mathbf{A} $ 가 어떤 요소로 이루어져 있는지 알아보는 방법에 대한 내용이다.
- $ \mathbf{I}_2 $ 는 identity matrix (항등 행렬)을 의미하고 $ \mathbf{e}_1, \mathbf{e}_2 $ 는 $ \mathbf{I}_2 $ 의 column을 의미한다.
- $ \mathbf{T}(\mathbf{x}) = \mathbf{A}\mathbf{x} $ 를 의미한다. $ \mathbb{R}^{2} $ domain 에서 $ \mathbb{R}^{3} $ codomain 으로 변환해주는 $ \mathbf{A} $ 를 모르고 $ \mathbf{T}( \mathbf{e}) $ (e 의 image)를 안다고 가정하면 이경우에 $ \mathbf{A} $ 가 무엇인지 찾을 수 있다.
항등 함수의 성질과 linear transformation 의 특성을 이용하면 다음과 같이 표현이 가능하다.
즉 이것을 통해 $ \mathbf{A} $ 는 $ \mathbf{T}( \mathbf{e}) $ 로 이루어져 있다는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
Theorem10.
\[T(\mathbf{x}) = A(\mathbf{x}) \quad for \; all \; \mathbf{x} \; in \; \mathbb{R}^{n}\]
Let $ \, T : \mathbb{R}^{n} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{m} $ be a linear transformation. Then there exists a unique matrix $ A $ such thatIn fact, $ \, A \, $ is the $ \, m \times n \, $ matrix whose $ j $ th column is the vector $ T(\mathbf{e}_j) $, where $ \mathbf{e}_j $ is the $ j $ th column of the identity matrix in $ \mathbb{R}^{n} $ :
\[A = \begin{bmatrix} T(\mathbf{e}_1) & \dots & T(\mathbf{e}_n) \end{bmatrix}\]
- $ T(\mathbf{e}) $ 로 구성된 $ A $ 를 standard matrix (표준 행렬) for the linear transformation $T$ 라고 부른다.
$ \mathbb{R}^{n} $ space 에 있는 identity matrix의 각각의 column을 transformation을 취한 결과 image 를 column으로 갖고있는 matrix를 standard matrix 라고 한다.
증명
- vector x 를 $ I_n \mathbf{x} $ 라고 표현해보자 여기서 $ I $ 는 identity matrix 이다.
아래 식은 $ \mathbf{x} $ 를 linear combination 형태로 표현한 것이다.
- $ A $ 는 $ T(e) $ 의 열들로 구성되어 있으므로 standard matrix 이다.
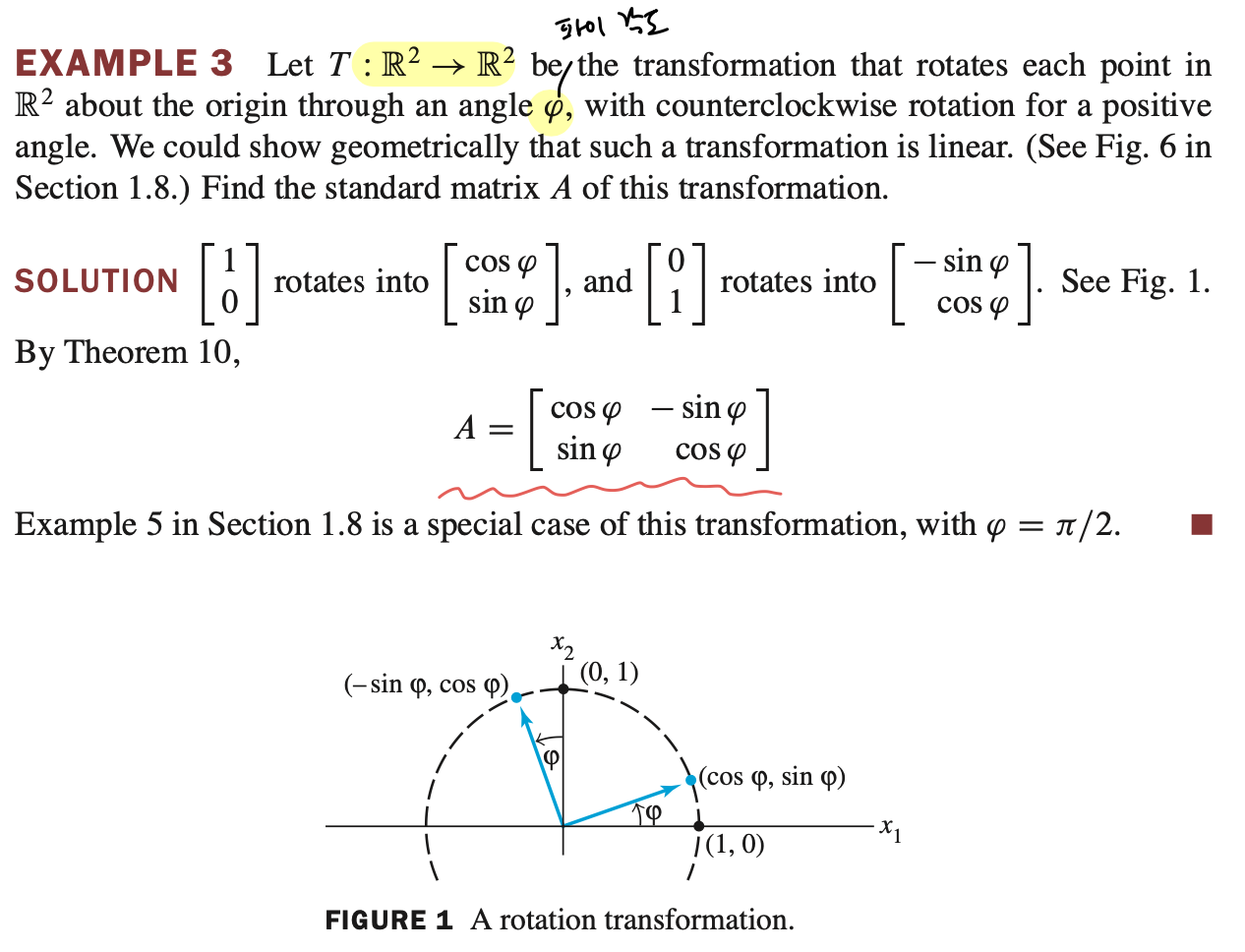
Standard Matrix Example
\[T : \mathbb{R}^{2} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{2}\]$T$ 는 $\mathbb{R}^{2}$ domain 에서 $\mathbb{R}^{2}$ codomain 으로 변환하는 함수이다.
- 위 그림처럼 반시계 방향으로 회전하는 transformation 을 찾아보자.
- Identity matrix 는 transformation 결과만 알면 transformation matrix 를 도출할 수 있다.
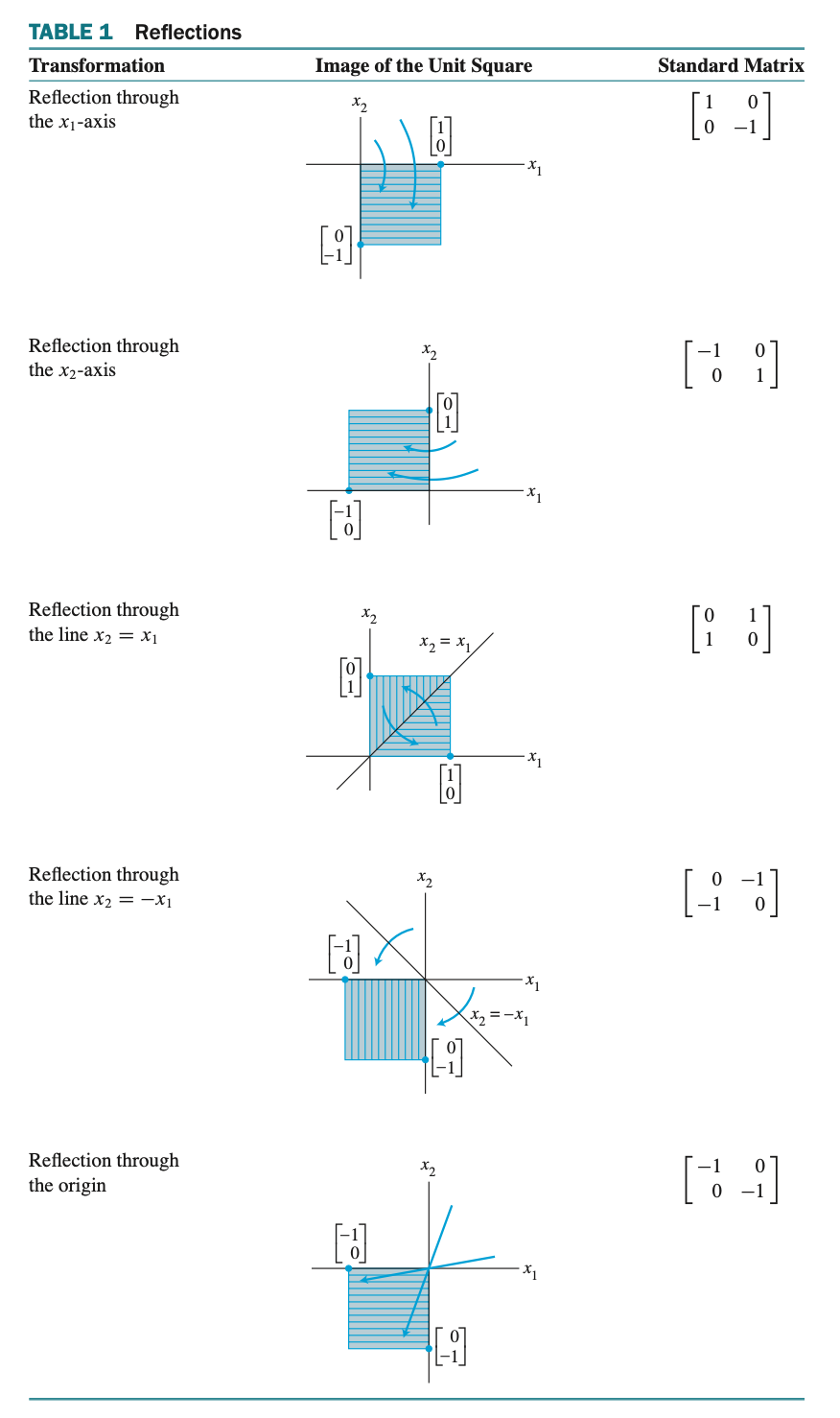
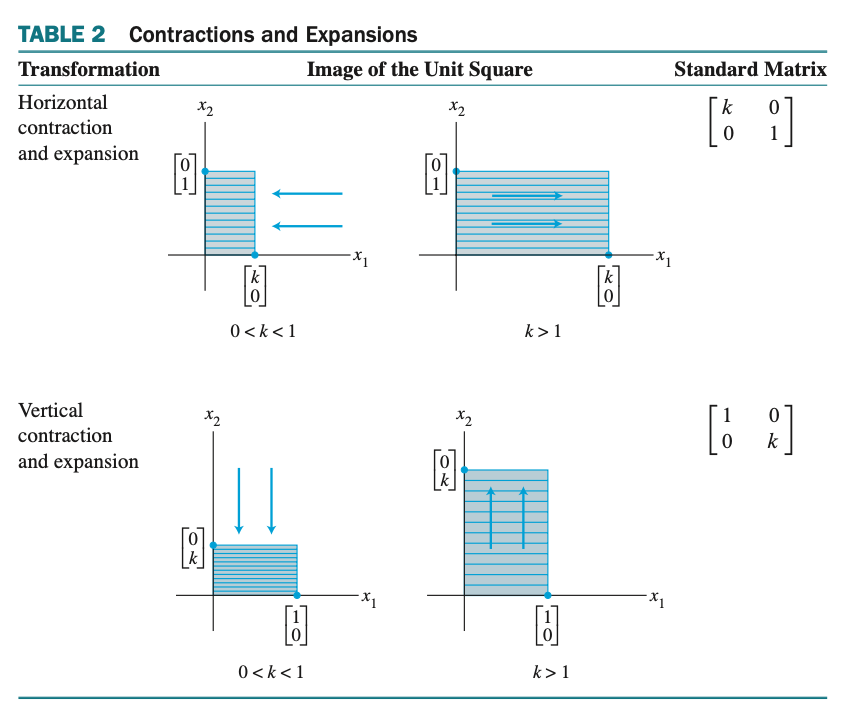
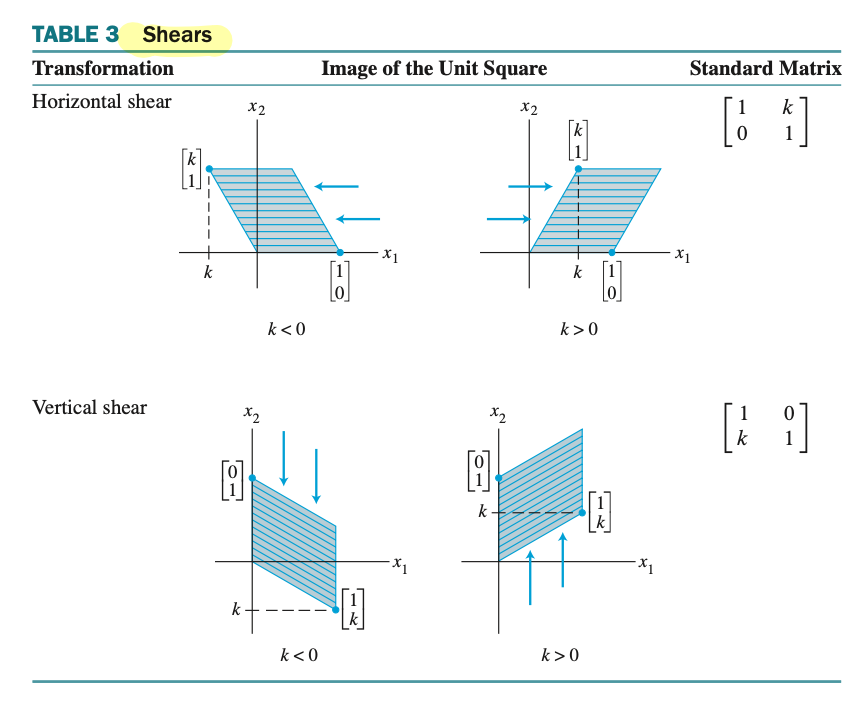
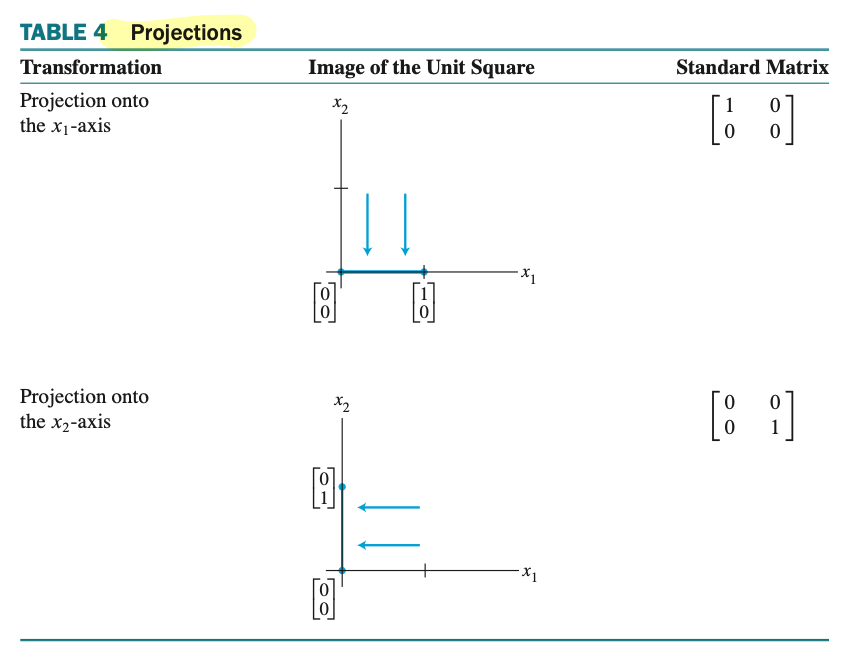
Geometric Linear Transformation of $\mathbb{R}^{2}$ - 2차원 실수 체계에서의 기하학적인 선형 변환
Onto - Surjective , 전사 함수
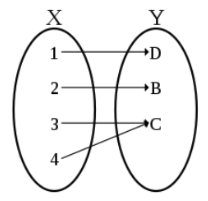
- Transformation 에서 중요한 단어 onto 와 one to one 2가지를 알아보자.
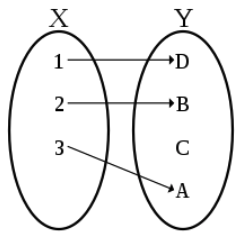
Onto 는 codomain의 임의의 $y$ 에 대해서 적어도 하나의 $x$ 가 대응된다는 것이다.
- 그림을 보면 3,4 가 C 에 겹쳐진다. 이를 Onto (one to one 일대일 대응이 아니다.)
이것을 Transformation 에 적용해보자.
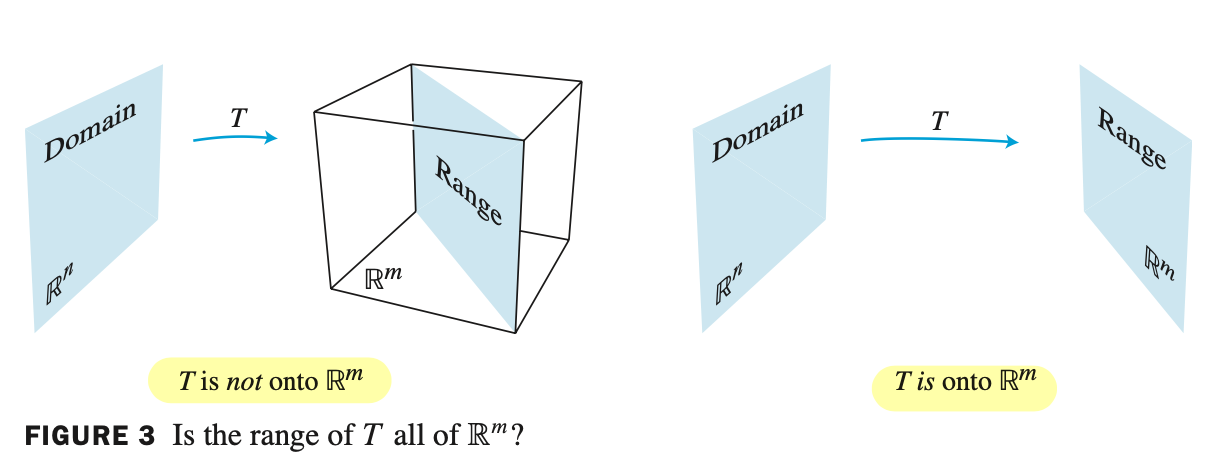
Does $T$ map $\mathbb{R}^{n}$ onto $\mathbb{R}^{m}$? 의미는 Does $T(x) = b$ have at least one solution for each $b$ in $\mathbb{R}^{m}$ 을 의미한다.
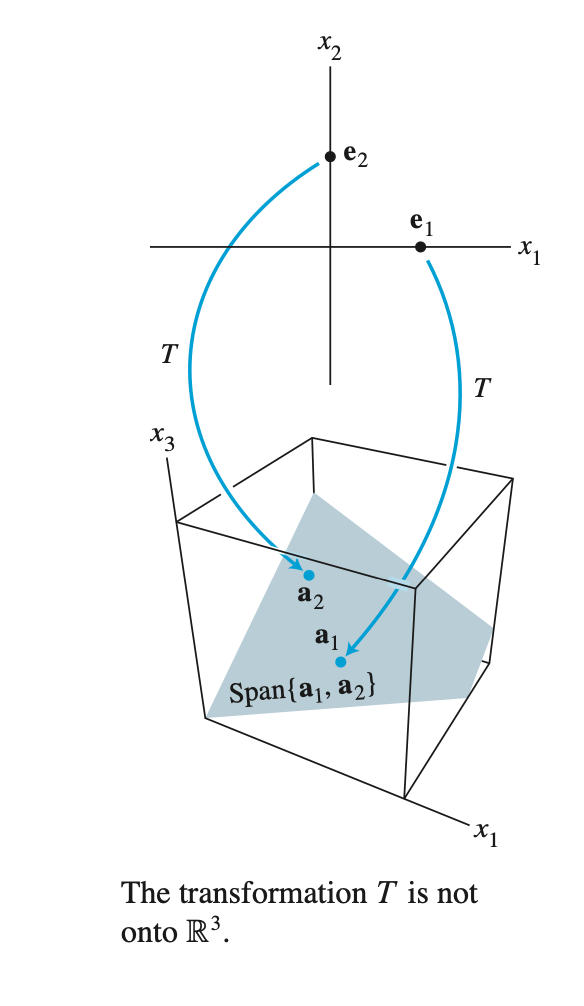
- $T$ 의 range(모든 image set)가 모두 codomain $\mathbb{R}^{m}$ 에 있을 때 $T$ 는 $\mathbb{R}^{m}$ 에 onto 한다.
즉, codomain $\mathbb{R}^{m}$ 에 있는 각각의 $b$ 에 대해 $ T(x) = b $ 의 적어도 하나의 solution이 존재한다면 onto 라고 할 수 있다.
- $\mathbb{R}^{m}$ 에서 $T(x)$ 가 $T$ 의 range에 포함되지 않는 경우가 있으면 not onto 이다.
- codomain $\mathbb{R}^{m}$ 전체가 range 그 자체면 onto 이다.
- 임의의 $b$ 에 대해 최소 1개의 solution 이 있으면 onto 이다.
One-to-one - Injection, 단사 함수
- domain(정의역)과 codomain(공역)이 원소 하나에 대응되는 것을 의미한다. 일대일 함수와는 살짝 다른 점은 Y원소 개수와 X원소 개수가 같을 필요가 없다는 점이다.
하지만, X원소 개수 $ <= $ Y원소 개수는 만족해야한다!
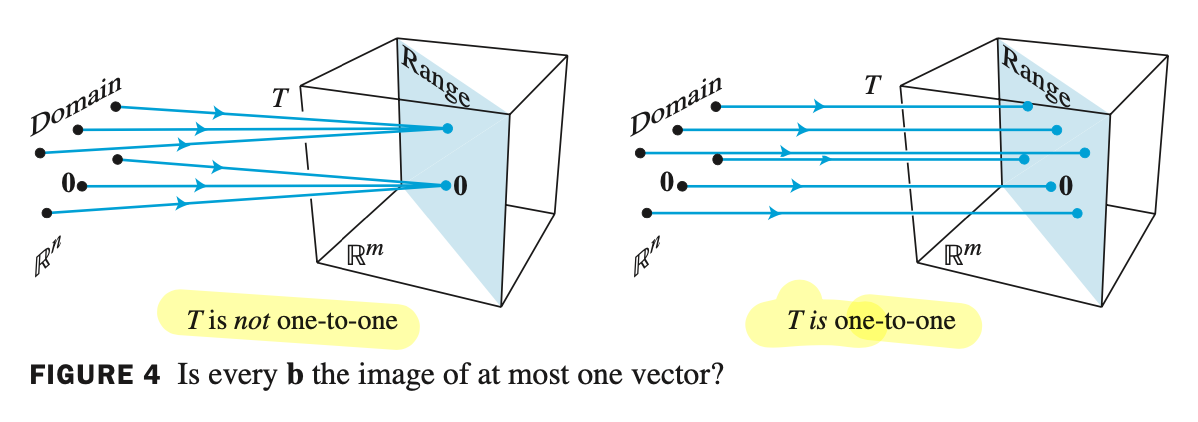
is $T$ one-to-one?의 의미는 Does $T(x) = b$ have either a unique solution or none at all? (해가 없거나 1개)를 의미한다.
- 1:1 매칭이면 $T$ is one-to-one
- 하나의 image 가 여러 개의 vector 에 해당된다면 $T$ is not one-to-one 이다.
onto 와 one-to-one 예제
- row 3개, pivot position 3개 있으므로 solution 이 존재한다. 무조건 solution 이 존재하므로 $\mathbb{R}^{4}$ 에서 $\mathbb{R}^{3}$ 으로 onto 한다.
- $x_3$ 는 free variable 이므로 infinitely many solution 이므로 not one-to-one 이다.
Theorem11.
Let $ \, T : \mathbb{R}^{n} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{m} $ be a linear transformation. Then $T$ is one-to-one if and only if the equation $ T(\mathbf{x}) = 0 $ has only the trivial solution.
- one-to-one 은 solution 이 최대 1개 또는 해가 없음을 의미한다.
theorem11 은 $T$ 가 one-to-one 이면, $ T(\mathbf{x}) = 0 $ 방정식은 trivial solution ($x=0$)만 갖는다는 정리이다.
- 증명
- $T$ is one-to-one 일 경우 trivial solution 만을 갖게 된다.
- 만약 $T$ is not one-to-one 인 경우 $T(u) = b$ , $T(v) = b$ one-to-one 이 아니므로 b(image)는 여러개의 vector 와 매칭된다. (해가 여러개)
- 위 식에서 one-to-one 이 아니므로 nontrivial solution 을 갖게 되어 $ \mathbf{u} - \mathbf{v} \ne 0 $ 을 성립한다. 따라서 $T(\mathbf{x}) = 0$ 은 1개 이상의 solution을 갖고있다.
Theorem12.
Let $ \, T : \mathbb{R}^{n} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{m} $ be a linear transformation, and let $A$ be the standard matrix for $T$. Then:a. $T$ maps $\mathbb{R}^{n}$ onto $\mathbb{R}^{m}$ if and only if the columns of $A$ span $\mathbb{R}^{m}$;
b. $T$ is one-to-one if and only if the columns of $A$ are linearly independent.
- $ \, T : \mathbb{R}^{n} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^{m} $ 이 linear transformation 이면 $A$ 는 $T$ 에 대한 standard matrix 이다.
$T$ 가 $\mathbb{R}^{n}$ onto $\mathbb{R}^{m}$ 이면 columns of $A$ 는 Span $\mathbb{R}^{m}$ 이다. 다르게 말하면, columns of $A$ 가 Span $\mathbb{R}^{m}$ 이면 $T$ 는 $\mathbb{R}^{n}$ onto $\mathbb{R}^{m}$ 이다.
- $T$ 가 one-to-one 이면 columns of $A$ 는 linearly independent 하다. 즉, trivial solution 만을 갖는다는 의미.