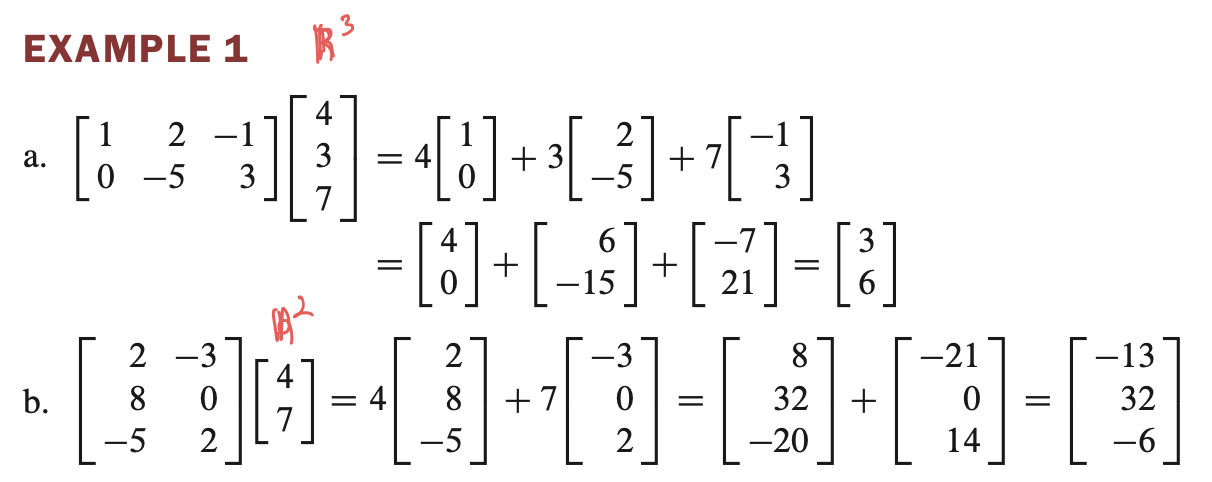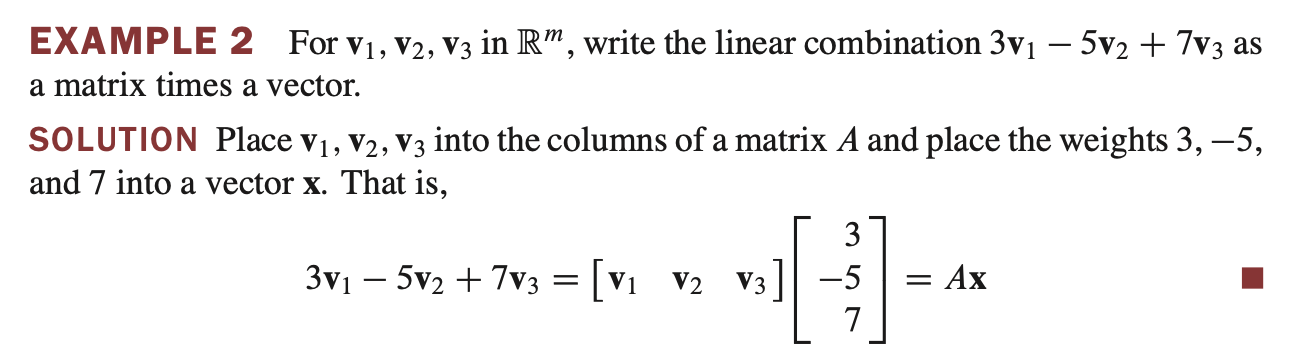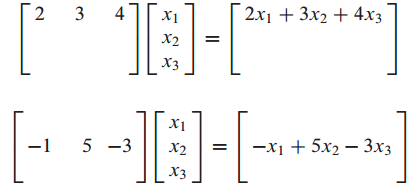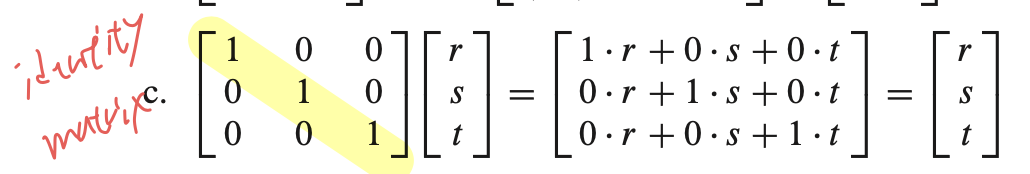Linear Algebra - 1.4 The Matrix Equation Ax=b
- Linear Algebra - 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations
- Linear Algebra - 1.2 Row Reduction and Echelon Forms
- Linear Algebra - 1.3 Vector Equations
- Linear Algebra - 1.4 The Matrix Equation Ax=b
- Linear Algebra - 1.5 Solution Sets of Linear Algebra
- Linear Algebra - 1.6 Linear Independence and Linear Dependence
- Linear Algebra - 1.7 Introduction to Linear Transformation
- Linear Algebra - 1.8 The Matrix of a Linear Transformation
- Linear Algebra - 2.1 Matrix Operations
- Linear Algebra - 2.2 The Inverse of Matrix
- Linear Algebra - 2.3 Characterizations of Invertible Matrices of
- Linear Algebra - 2.4 Partitioned Matrices
- Linear Algebra - 2.5 Matrix Factorizations, LU Decomposition
- Linear Algebra - 2.6 Subspaces of $\mathbb{R}^n$
- Linear Algebra - 2.7 Dimension and Rank
- Linear Algebra - 3.1 Introduction to Determinants
- Linear Algebra - 3.2 Properties of Determinants
- Linear Algebra - 3.3 Cramer's Rule, Volume, And Linear Transformations
- Linear Algebra - 4.1 Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues
- Linear Algebra - 4.2 The Characteristic Equation
- Linear Algebra - 4.3 Diagonalization
- Linear Algebra - 4.4 Eigenvectors And Linear Transformations
- Linear Algebra - 4.5 Complex Eigenvalues
- Linear Algebra - 5.1 Inner Product And Orthogonality
- Linear Algebra - 5.2 Orthogonal Sets
- Linear Algebra - 5.3 Orthogonal Projections
- Linear Algebra - 5.4 The Gram-Schmidt Process (그람 슈미츠 과정)
- Linear Algebra - 5.5 Least-Square Problems
- Linear Algebra - 6.1 Diagonalization of Symmetric Matrices
- Linear Algebra - 6.2 Quadratic Forms
- Linear Algebra - 6.3 Constrained Optimization
- Linear Algebra - 6.4 SVD, The Singular Value Decomposition
- Linear Algebra - 6.5 Reduced SVD, Pseudoinverse, Matrix Classification, Inverse Algorithm
용어 정리
- matrix equation (행렬 방정식)
- $ Ax = b $
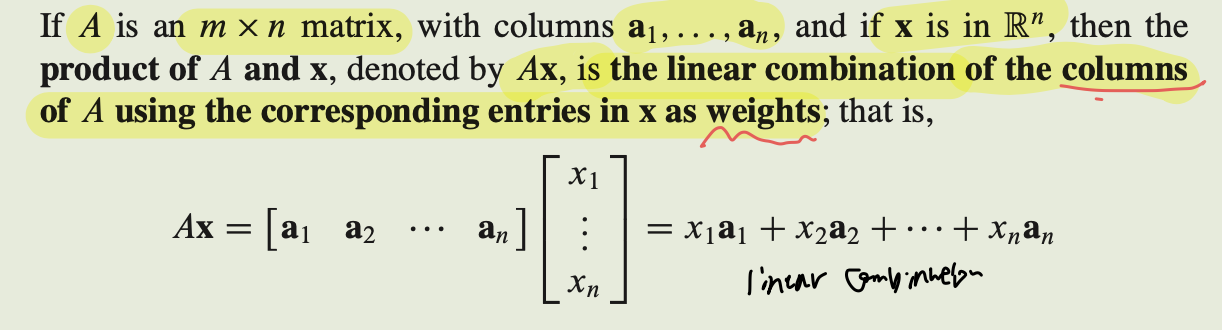
Product of A and X
- x를 weights로 사용한 A의 columns의 linear combination이다.
- 즉, x는 scalar의 vector 이다.
Matrix equation 풀기
Vector equation to matrix equation - 벡터 방정식을 행렬 방정식으로 표현
벡터 방정식을 행렬 방정식으로 표현할 수 있다.
- linear combination을 matrix equation 으로 표현할 수 있다.
- 일반화 했을 경우.. $ x_1v_1 + x_2v_2 + x_3v_3 = \begin{bmatrix} v_1, v_2, v_3 \; \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} x_1 \\ x_2 \\ x_3 \; \end{bmatrix} $
System of linear equations to matrix equation - 선형 시스템을 행렬 방정식으로 표현
More efficient way to compute matrix equation
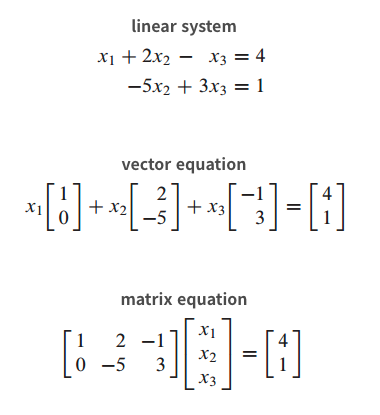
Theorem3. linear system 의 3가지 표현 방법
\[A\mathbf{x} = \mathbf{b}\]
If $ A $ is a $ m \times n $, with columns $ \mathbf{a_1}, \dots, \mathbf{a_n} $, and if $ \mathbf{b} $ is in $ \mathbb{R}^{m} $, the matrix equationhas the same solution set as the vector equation
\[x_1\mathbf{a_1} + x_2\mathbf{a_2} + \dots + x_n\mathbf{a_n} = \mathbf{b}\]which, in turn, has the same solution set as the system of linear equation whose augmented matrix is
\[\begin{bmatrix} a_1 & a_2 & \dots & a_n & b \; \end{bmatrix}\]
- linear system을 3가지로 표현할 수 있으며 이 3가지는 모두 동일한 solution set을 갖는다!!
Theorem4. A의 필요충분조건 if and only if
Let $ A $ be an $ m \times n $ matrix. Then the following statements are logically equivalent.
That is, for a particular $ A $ , either they are all true statements or they are all false.a. For each $ \mathbf{b} $ in $ \mathbb{R}^{m} $ , the equation $ Ax = mathbf{b} $ has a solution.
b. Each $ \mathbf{b} $ in $ \mathbb{R}^{m} $ is a linear combination of the columns of $ A $.
c. The columns of $ A $ span $ \mathbb{R}^{m} $.
d. $ A $ has a pivot position in every row.
- 4가지 조건 중 하나라도 True 이면 모두 True, 하나라도 False 이면 모두 False.
a. For each $ \mathbf{b} $ in $ \mathbb{R}^{m} $ , the equation $ Ax = mathbf{b} $ has a solution.
- $ \mathbb{R}^{m} $ 공간에 있는 임의의 b에 대해서 matrix equation 인 $ Ax = b $ 는 solution 을 갖고 있다.
b. Each $ \mathbf{b} $ in $ \mathbb{R}^{m} $ is a linear combination of the columns of $ A $.
- $ \mathbb{R}^{m} $ 공간에서 b는 A의 columns의 선형 결합이다.
c. The columns of $ A $ span $ \mathbb{R}^{m} $.
- A의 열들은 $ \mathbb{R}^{m} $ 공간에서 span 하다 -> linear combination을 의미
d. $ A $ has a pivot position in every row.
- A는 모든 행에 pivot position을 갖고 있다.
- A는 coefficient matrix를 의미한다. (주의, A는 augmented matrix가 아니다.)
- A의 행에 pivot position이 없다면 b가 pivot position 이 되고 이는 no solution을 의미한다.
$ \begin{bmatrix} \; 0 & \dots & 0 & \mathbf{b} \; \end{bmatrix} $ with $ \mathbf{b} $ is nonzero 가 되면 안된다.
Identity matrix 를 곱하면?
- 위 그림에서 대각선이 모두 1이고, 나머지는 0인 행렬을 identity matrix 줄여서 $ I $ 라고 한다.
- $ Ix = x $ for every $ x $ in $ \mathbb{R}^{3} $.
Theorem5.
If $ A $ is an $ m \times n $ matrix, $ \mathbf{v} $ and $ \mathbf{v} $ are vectors in $ \mathbb{R}^{n} $, and $ c $ is a scalar, then:a. $ A(\mathbf{u} + \mathbf{v}) = A\mathbf{u} + A\mathbf{v}; $
b. $ A(c\mathbf{u}) = c(A\mathbf{u}) $
- 여기서 A는 coefficient matrix 이다.
- u, v는 벡터
- c 는 스칼라