Linear Algebra - 6.3 Constrained Optimization
- Linear Algebra - 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations
- Linear Algebra - 1.2 Row Reduction and Echelon Forms
- Linear Algebra - 1.3 Vector Equations
- Linear Algebra - 1.4 The Matrix Equation Ax=b
- Linear Algebra - 1.5 Solution Sets of Linear Systems
- Linear Algebra - 1.6 Linear Independence and Linear Dependence
- Linear Algebra - 1.7 Introduction to Linear Transformation
- Linear Algebra - 1.8 The Matrix of a Linear Transformation
- Linear Algebra - 2.1 Matrix Operations
- Linear Algebra - 2.2 The Inverse of Matrix
- Linear Algebra - 2.3 Characterizations of Invertible Matrices of
- Linear Algebra - 2.4 Partitioned Matrices
- Linear Algebra - 2.5 Matrix Factorizations, LU Decomposition
- Linear Algebra - 2.6 Subspaces of $\mathbb{R}^n$
- Linear Algebra - 2.7 Dimension and Rank
- Linear Algebra - 3.1 Introduction to Determinants
- Linear Algebra - 3.2 Properties of Determinants
- Linear Algebra - 3.3 Cramer's Rule, Volume, And Linear Transformations
- Linear Algebra - 4.1 Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues
- Linear Algebra - 4.2 The Characteristic Equation
- Linear Algebra - 4.3 Diagonalization
- Linear Algebra - 4.4 Eigenvectors And Linear Transformations
- Linear Algebra - 4.5 Complex Eigenvalues
- Linear Algebra - 5.1 Inner Product And Orthogonality
- Linear Algebra - 5.2 Orthogonal Sets
- Linear Algebra - 5.3 Orthogonal Projections
- Linear Algebra - 5.4 The Gram-Schmidt Process (그람 슈미츠 과정)
- Linear Algebra - 5.5 Least-Square Problems
- Linear Algebra - 6.1 Diagonalization of Symmetric Matrices
- Linear Algebra - 6.2 Quadratic Forms
- Linear Algebra - 6.3 Constrained Optimization
- Linear Algebra - 6.4 SVD, The Singular Value Decomposition
- Linear Algebra - 6.5 Reduced SVD, Pseudoinverse, Matrix Classification, Inverse Algorithm
용어 정리
- Quadratic Forms - 이차 형식
- Constrained Optimization - 구속 최적화
Constrained Optimization - 구속 최적화
- Constrained Optimization 은 quadratic form $ Q(\mathbf{x}) = \mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{x} $ 에서 maximum(최대값)과 minimum(최소값)을 찾고 싶을 때
모든 $\mathbf{x}$ 영역에서 찾는 것이 아니라 어떤 제약 조건을 줬을 때, 그 조건 하에서의 maximum과 minimum 을 찾는 방법이다.
- constraint 다음과 같이 제약 조건을 준다.
- 위 식을 다른 말로 하면 $\mathbf{x}$ 의 norm 또는 lehgth 가 1이라는 것과 동일하다.
- $\mathbb{R}^n$ space 에 있는 $\mathbf{x}$ 의 dot product 가 1일 때 이 제약 조건 하에서 maximum 과 minimum 은 어떻게 되는지 다음 예제를 통해서 파악해보자.
Example 1
Find the maximum and minimum values of $\; Q(\mathbf{x}) = 9x_1^2 + 4x_2^2 + 3x_3^2 \;$ subjected to the constraint $\; \mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{x} = 1$
quadratic form : $ Q(\mathbf{x}) = 9x_1^2 + 4x_2^2 + 3x_3^2 $
constraint : $ \mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{x} = 1 $
따라서 $x_2^2, x_3^2$ 은 nonnegative 이므로 다음 조건이 성립한다.
- 따라서 다음식이 성립한다.
- $\mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{x} = 1$ 이라는 조건 때문에 $Q(\mathbf{x})$ 의 maximum 값은 9를 초과할 수 없다.
- 따라서 $\mathbf{x} = (1,0, 0)$ 혹은 -1을 scale 한 $(-1,0, 0)$ 일 때, $Q(\mathbf{x}) = 9$ 가 되고 9가 maximum 최대값이 된다.
- minimum 을 구하려면 다음 조건이 성립한다.
- 여기서 $Q(\mathbf{x})$ 는 제약조건 하에 3 미만의 값을 가질 수 없으므로 $\mathbf{x} = (0 ,0, 1)$ 일 때 $Q(\mathbf{x}) = 3$ 이 minimum 최소값이 된다.
- 또한 eigenvalue 의 maximum, minimum 과 constraint quadratic form 의 maximum, minimum 이 동일하다는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
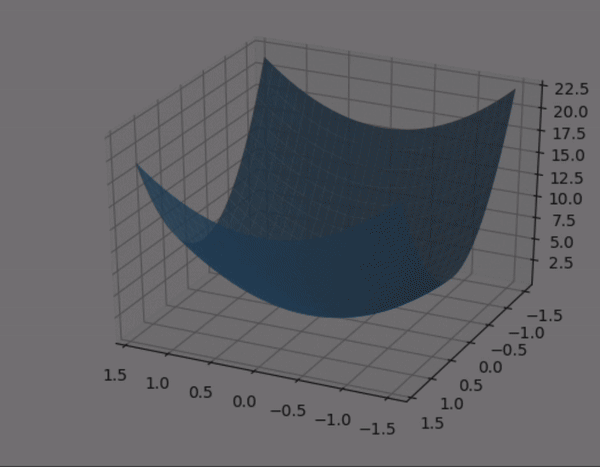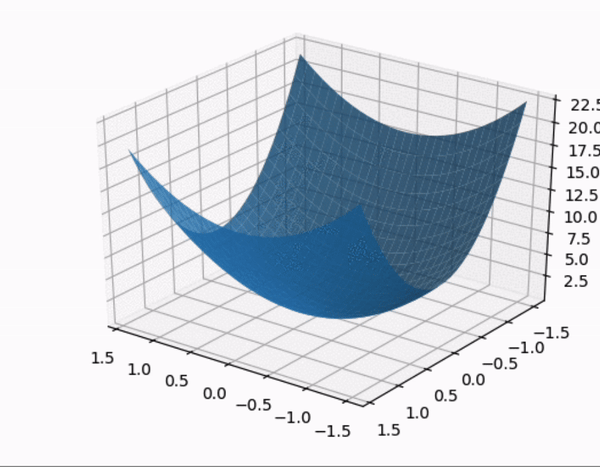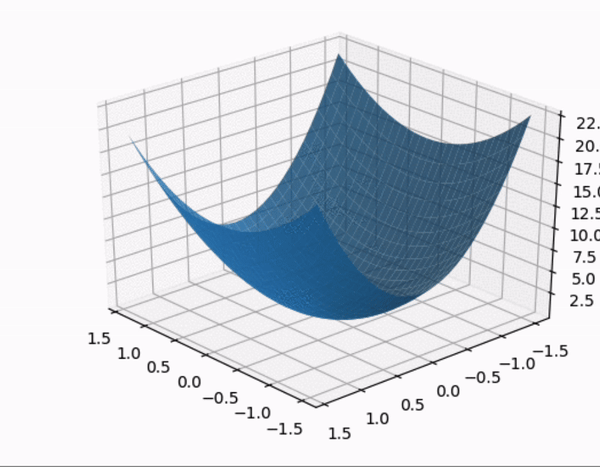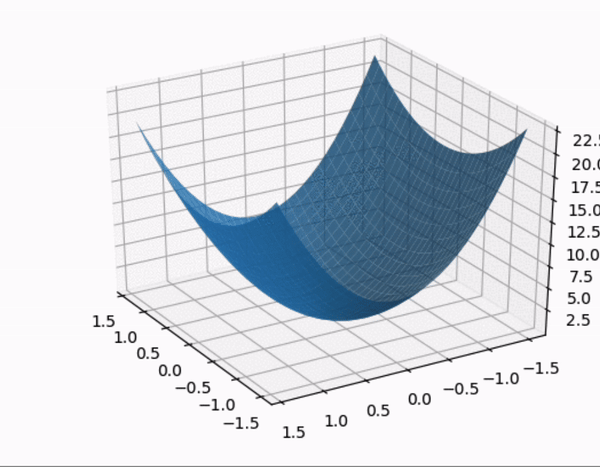
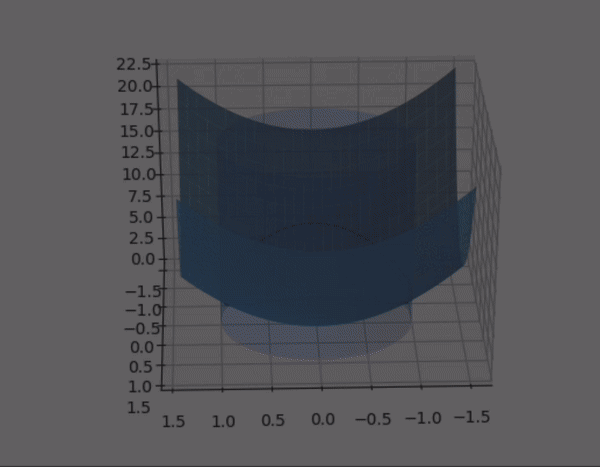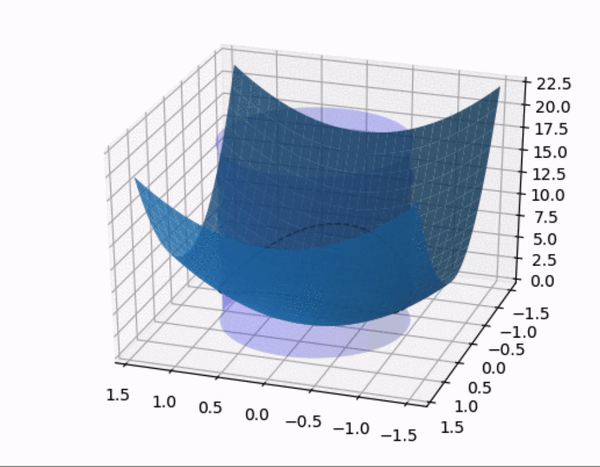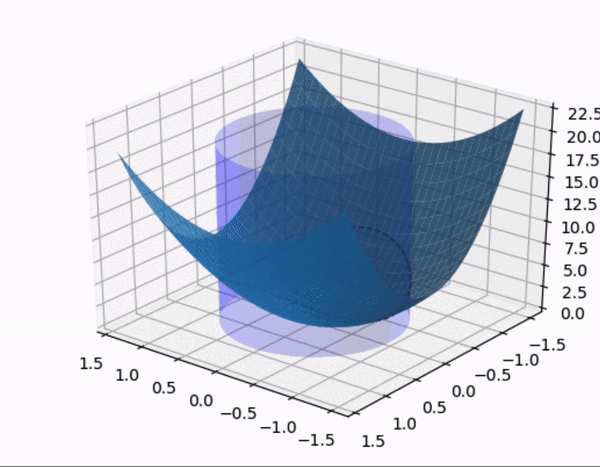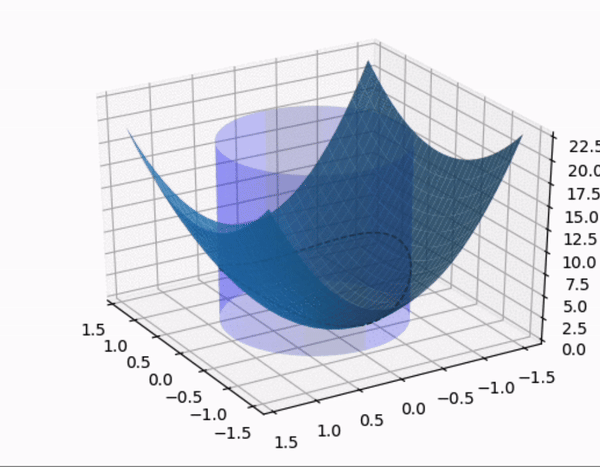
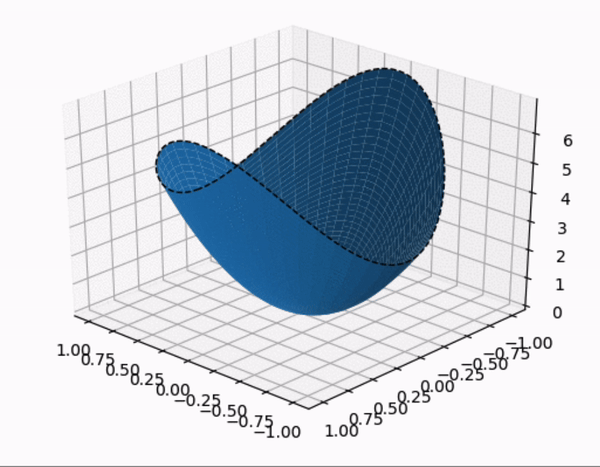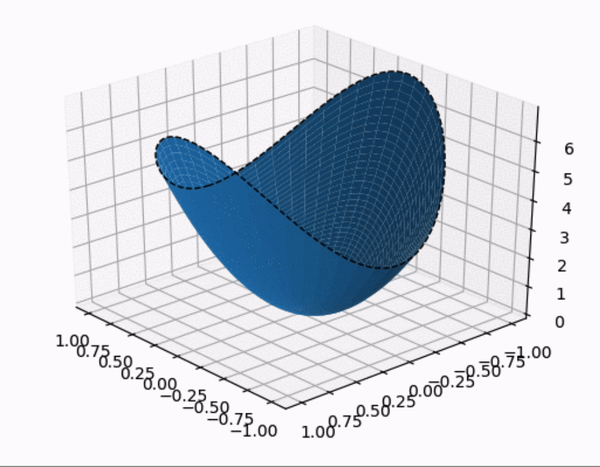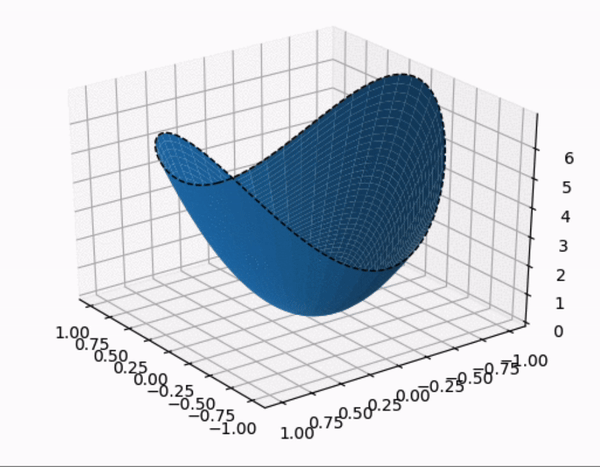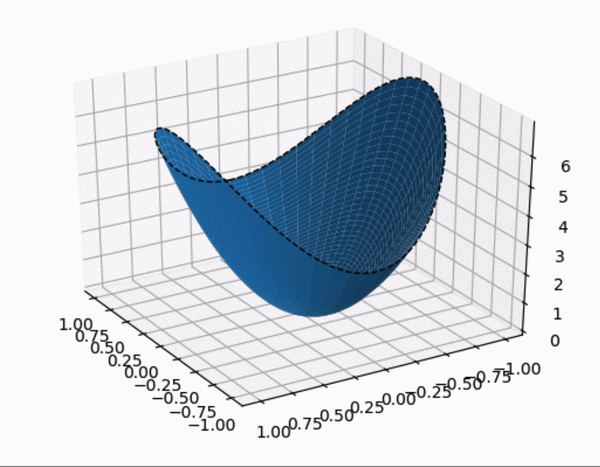
- constrained optimization 을 시각적으로 살펴보자.
- quadratic form 의 행렬 $A$ 가 다음과 같이 주어졌을 때,quadratic form 과 constraint 제약 조건 하에 quadratic form 을 시각화 한 것이다.
- constraint
- $A$ 의 eigenvalue 는 $A$ 가 diagonal matrix 이므로 $\lambda = 3, 7$
- 따라서 maximum : 7, minimum :3 이 된다. 또한 여기서 $z$ 축이 $\; Q(\mathbf{x})$ 를 의미한다.
- (1) $\quad Q(\mathbf{x})$
- (2) $\quad Q(\mathbf{x})$ , $\mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{x} = 1$
- $\mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{x} = 1$ 부분을 제외한 영역을 잘라서 표현한 그림
Theorem6.
Let $A$ be a symmetric matrix. $M$ is the greatest eigenvalue $\lambda _1$ of $A$ and $m$ is the least eigenvalue of $A$ . The value of $\mathbf{x}^TA\mathbf{x}$ is $M$ when $\mathbf{x}$ is a unit eigenvector $\mathbf{u}_1$ corresponding to $M$ . The value of $\mathbf{x}^TA\mathbf{x}$ is $m$ when $\mathbf{x}$ is a unit eigenvector corresponding to $m$ .
- $A$ 가 symmetric matrix 이고 $M$ 은 $A$ 의 가장 큰 eigenvalue, $m$ 은 $A$ 의 가장 작은 eigenvalue 로 표기하면
- $\mathbf{x}$ 가 $M$ 에 해당하는 unit eigenvector 일 때, quadratic form 의 값은 $M$ 이다.
- $\mathbf{x}$ 가 $m$ 에 해당하는 unit eigenvector 일 때, quadratic form 의 값은 $m$ 이다.
- 증명
- $A$ 가 symmetric matrix 이면 orthogonally diagonalize 가 가능하므로 $A = PDP^{-1}$ 이 된다.
- 위 식은 다음과 같다
$\lVert \mathbf{x} \rVert = \lVert \mathbf{y} \rVert $ 가 되는 이유는 다음과 같다.
\(P^TP = I\) 이므로
특히 $\lVert \mathbf{x} \rVert = 1$ 과 $\lVert \mathbf{y} \rVert = 1$ 는 동치이므로 $\lVert \mathbf{x} \rVert = \lVert \mathbf{y} \rVert $ 가 성립한다.
$D = \begin{bmatrix} \lambda _1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & \lambda _2 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & \lambda _3 \end{bmatrix} $ 이고 $\lambda _1 \ge \lambda _2 \ge \lambda _3$ 임을 가정하면
그러므로 maximum 인 $M \le \lambda _1$ 이고 $\mathbf{y} = \mathbf{e} _1 = (1,0,0)$ unit vector 로 둘 경우 $M = \lambda _1$ 이 된다.
$\mathbf{x} = P\mathbf{e} _1 = \begin{bmatrix} \mathbf{u}_1 & \mathbf{u}_2 & \mathbf{u}_3 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 0 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} = \mathbf{u}_1 $
Example 2
Let $A = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & 2 & 1 \\ 2 & 3 & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & 4 \end{bmatrix} $ . Find the maximum value of the quadratic from $\mathbf{x}^TA\mathbf{x}$ subject to constraint $\mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{x} = 1$ , and find a unit vector at which this maximum value is attained.
- 여기서 행렬 $A$ 가 주어졌을 때, quadratic form 인 $\mathbf{x}^TA\mathbf{x}$ 의 최대값을 찾고 그에 해당하는 unit eigenvector 를 찾는 문제이다.
quadratic form 의 constraint 는 $\mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{x} = 1$ 로 주어졌다.
- 우선, characteristic equation 을 사용하여 $A$ 의 eigenvalue 들을 찾아야한다.
- maximum eigenvalue 는 6 이므로 quadratic form 의 maximum 은 6이다.
또한 $(A - 6I) = 0$ 를 augmented matrix 로 만들어 row reduction 을 하여 general solution 으로 표현하면, eigenvalue 6 에 해당하는 eigenvector 를 구할 수 있다.
\(\lambda = 6\) 의 eigenvector $ \begin{bmatrix} 1 \\ 1 \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} $
- 여기서 normalize 를 취해주면 다음과 같이 unit eigenvector 를 구할 수 있다. 추가적으로 마이너스 부호가 붙어도 같은 값이다. $-\mathbf{u}_1$
Theorem7.
Let $A, \lambda _1, \; \mbox{and} \; \mathbf{u}_1$ be as in Theorem 6. Then the maximum value of $\mathbf{x}^TA\mathbf{x}$ subject to the constraints
\[\mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{x} = 1, \quad \mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{u}_1 = 0\]is the second greatest eigenvalue, $\lambda _2$ , and this maximum is attained when $\mathbf{x}$ is an eigenvector $\mathbf{u}_2$ corresponding to $\lambda _2$ .
- $A$ 행렬의 maximum eigenvalue 에 해당하는 unit eigenvector 가 $\mathbf{u}_1$ 이였다.
- 여기서 $\mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{u} = 0$ 이라는 조건은 $\mathbf{u}_1 = 0$ 임을 의미한다.
- 이 경우에는 두 번째로 큰 eigenvalue 가 quadratic form 의 maximum 이 된다.
- 여기서 $\mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{u} = 0$ 이면 $\mathbf{u}_1 = 0$ 이므로 $\lambda _1$ 은 빼고 생각해줘야한다. 따라서 그 다음으로 큰 $\lambda _2$ 가 maximum 이 되는 것이다.
Theorem8.
Let $A$ be a symmetric $n \times n$ matrix with an orthogonal diagonalization $\; A = PDP^{-1} \;$ , where the entries on the diagonal of $D$ are arranged so that $ \; \lambda _1 \ge \lambda _2 \ge \dots \ge \lambda _n \;$ and when the columns of $P$ are corresponding unit eigen-vectors $\; \mathbf{u}_1 , \dots , \mathbf{u}_n \;$ Then for $\; k = 2, \dots , n \;$ , the maximum value of $\mathbf{x}^TA\mathbf{x}$ subject to the constraints
\[\mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{x} = 1 \; , \quad \mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{u}_1 = 0 \; , \quad \dots \; , \quad \mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{u}_{k-1} = 0\]is the eigenvalue $\lambda _k$ , and this maximum is attained at $\mathbf{x} = \mathbf{u}_k$ .
- 정리8은 정리7을 확장한 개념이다. 제약 조건을 더 늘렸다고 생각하면 된다.
- 제약 조건이 추가적으로 $\mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{u}_{k-1}$ 까지 주어졌을 때, $\mathbf{x}$ 가 $\mathbf{u}_k$ 이면 quadratic form 은 최대값이 된다. 그리고 그 최대값은 $\mathbf{u}_k$ 에 해당하는 eigenvalue 가 된다.
Example 3
Let $A = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & 2 & 1 \\ 2 & 3 & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & 4 \end{bmatrix} $ . Find the maximum value of the quadratic from $\mathbf{x}^TA\mathbf{x}$ subject to constraint $\mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{x} = 1 \; \mbox{and} \; \mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{u}_1 = 0 $ where $\mathbf{u}_1$ is a unit eigenvector corresponding to the greatest eigenvalue of $A$ , and find a unit vector at which this maximum value is attained.
- characteristic equation 을 통해 eigenvalue 를 찾으면
- 여기서 정리 7에 의해 $\mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{u}_1 = 0$ 이므로 $\mathbf{u}_1 = 0$ 이 되므로 $\lambda _2$ 가 maximum 이 된다.
- 위 식을 풀어서 normalize 를 해주면 unit eigenvector 를 구할 수 있다.
Example 4
Let $A = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & -2 & 4 \\ -2 & 6 & 2 \\ 4 & 2 & 3 \end{bmatrix} $ . Find the maximum value of the quadratic from $\mathbf{x}^TA\mathbf{x}$ subject to constraint $\mathbf{x}^T\mathbf{x} = 1 $ , and find a unit vector at which this maximum value is attained.
- $A$ 행렬은 symmetric matrix 이므로 orthogonally diagonalize 하므로 $A = PDP^{-1}$ 형태로 분해를 해주자.
- characteristic equation 으로 eigenvalue 와 eigenvector 를 구하여 $P, D$ 행렬을 만들어주면 다음과 같다.
여기서 $\lambda = 7$ with multiplicity $= 2$ 인 형태 즉 중복이 된다. 이럴 때는 unit eigenvector 가 Span{$\mathbf{u}_1, \mathbf{u}_2$} 이다.
임의의 벡터 $\mathbf{v} = \alpha \mathbf{u}_1 + \beta \mathbf{u}_2$ 와 $\alpha ^2 + \beta ^2 = 1$ 이라는 조건을 줬을 때, 피타고라스 정리를 사용할 수 있는데 이는 $\mathbf{u}_1, \mathbf{u}_2$ 가 서로 orthonormal 한 관계에 있기 때문에 가능하다.
- 따라서 $\mathbf{v}^TA\mathbf{v}$ 를 생각해보면 다음과 같다. 여기서 $\mathbf{v}$ 는 $\mathbf{u}_1, \mathbf{u}_2$ 의 linear combination 이므로 다음과 같이 정리가 가능하다. 또한 $A\mathbf{v}$ 는 eigenvalue 정의에 의해 $A\mathbf{v} = \lambda \mathbf{v}$ 로 표현이 가능하므로..
- 여기서 $\lambda _1 = \lambda _2$ 는 multiplicity $= 2$ 인 중복된 상황이므로
- $(\alpha \mathbf{u}_1 + \beta \mathbf{u}_2 ) $ 는 $\mathbf{v}$ 의 linear combination 이므로
- 제약 조건 하에서 quadratic form 의 최대값은 7이라는 의미가 된다.