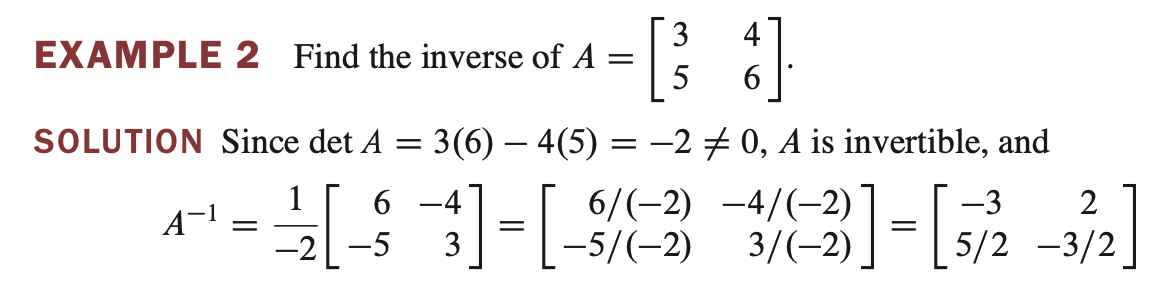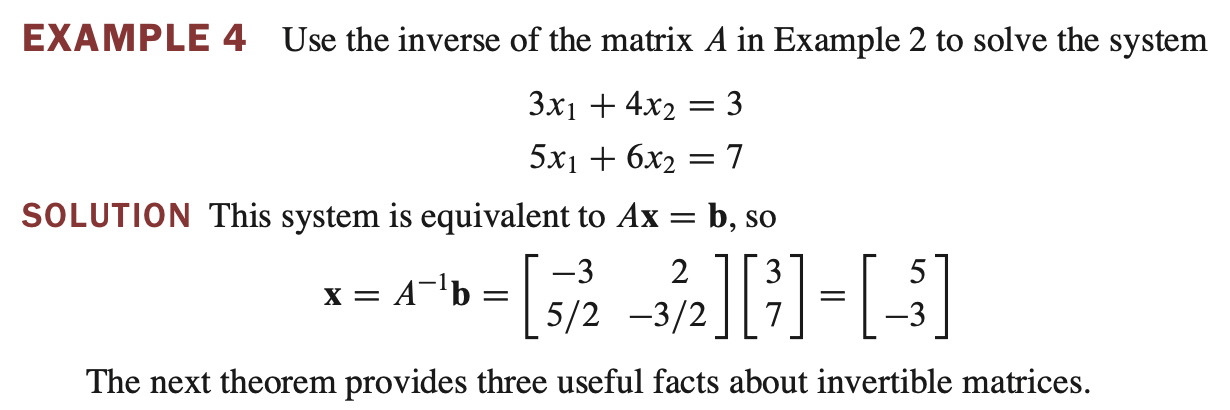Linear Algebra - 2.2 The Inverse of Matrix
- Linear Algebra - 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations
- Linear Algebra - 1.2 Row Reduction and Echelon Forms
- Linear Algebra - 1.3 Vector Equations
- Linear Algebra - 1.4 The Matrix Equation Ax=b
- Linear Algebra - 1.5 Solution Sets of Linear Systems
- Linear Algebra - 1.6 Linear Independence and Linear Dependence
- Linear Algebra - 1.7 Introduction to Linear Transformation
- Linear Algebra - 1.8 The Matrix of a Linear Transformation
- Linear Algebra - 2.1 Matrix Operations
- Linear Algebra - 2.2 The Inverse of Matrix
- Linear Algebra - 2.3 Characterizations of Invertible Matrices of
- Linear Algebra - 2.4 Partitioned Matrices
- Linear Algebra - 2.5 Matrix Factorizations, LU Decomposition
- Linear Algebra - 2.6 Subspaces of $\mathbb{R}^n$
- Linear Algebra - 2.7 Dimension and Rank
- Linear Algebra - 3.1 Introduction to Determinants
- Linear Algebra - 3.2 Properties of Determinants
- Linear Algebra - 3.3 Cramer's Rule, Volume, And Linear Transformations
- Linear Algebra - 4.1 Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues
- Linear Algebra - 4.2 The Characteristic Equation
- Linear Algebra - 4.3 Diagonalization
- Linear Algebra - 4.4 Eigenvectors And Linear Transformations
- Linear Algebra - 4.5 Complex Eigenvalues
- Linear Algebra - 5.1 Inner Product And Orthogonality
- Linear Algebra - 5.2 Orthogonal Sets
- Linear Algebra - 5.3 Orthogonal Projections
- Linear Algebra - 5.4 The Gram-Schmidt Process (그람 슈미츠 과정)
- Linear Algebra - 5.5 Least-Square Problems
- Linear Algebra - 6.1 Diagonalization of Symmetric Matrices
- Linear Algebra - 6.2 Quadratic Forms
- Linear Algebra - 6.3 Constrained Optimization
- Linear Algebra - 6.4 SVD, The Singular Value Decomposition
- Linear Algebra - 6.5 Reduced SVD, Pseudoinverse, Matrix Classification, Inverse Algorithm
용어 정리
- Invertible Matrix (역행렬이 존재하는 행렬)
- determinant (결정자)
- Elementary Matrix (기본 행렬)
Multiplicative Inverse of a Number
- Invertible Matrix 를 알아보기 전에 숫자의 승수 역수를 살펴보자. $5$의 역수는 $5^-1$ 이다.
Invertible Matrix
An $n \times m$ matrix $A$ is said to be invertible if there is an $n \times m$ matrix $C$ such that
\(CA = I \quad and \quad AC = I\)
- invertible 의 첫 번째 조건은 row와 column의 size가 동일해야 한다. 또한 $AC = I$ 인 $C$ 행렬이 있어야 하며 $C$는 unique (유일하다) 하다.
\[A^{-1}A = I \quad and \quad AA^{-1} = I\]
- matrix가 not invertible 이면 singular matrix (해가 존재하지 않는 행렬) 이다.
후반에서 singular matrix 형태로 나오면 역행렬을 사용해서 해를 구할 수 없는 어려움을 겪는다고한다..
- invertible 이면 nonsingular matrix (해가 존재) 이다.
Theorem4.
\[A^{-1} = {1 \over {ad-bc}} \begin{bmatrix} \phantom{-}d & -b \; \\\ -c & \phantom{-}a \; \end{bmatrix}\]
Let $ A = \begin{bmatrix} a & b \\ c & d \end{bmatrix} $ . If $ ad - bc \ne 0 $ , then $A$ is invertible andIf $ ad - bc = 0 $ , then $A$ is not invertible.
- $A$ 가 2x2 행렬일 때, $ ad - bc \ne 0 $ 이면 $A$는 invertible 하다.
$ ad - bc = 0 $ 이면 not invertible 하다.
- 여기서 <span style=”color:#179CFF”$ad - bc$> 는 pivot position 이 2개 있을 조건을 의미하며 determinant (결정자) </span> 라고 부른다.
어떤 matrix 가 invertible 을 판단할 때 determinant 가 0인지 아닌지를 확인하면 된다!
Theorem5.
If $A$ is an invertible $n \times n$ matrix, then for each $\mathbf{b}$ in $ \mathbb{R}^{n} $, the equation $A\mathbf{x} = \mathbf{b}$ has the unique solution $ \mathbf{x} = A^{-1}\mathbf{b} $.
- $A$ 가 invertible $n \times n$ matrix 이면 $ \mathbb{R}^{n} $ space 에 있는 $\mathbf{b}$ 에 대한 방정식 $A\mathbf{x} = \mathbf{b}$ 는 유일한 해 ( $ \mathbf{x} = A^{-1}\mathbf{b} $ )를 갖는다.
다시말해서, $A\mathbf{x} = \mathbf{b}$ 라는 방정식에서 $A$ 의 역행렬 $A^{-1}$ 은 단 하나만 존재한다는 것이다. $ A^{-1}\mathbf{b} $ is solution.
-증명
- 역행렬이 유일하다는 것을 증명하기 위해 다른 솔루션 u가 존재하는지 확인해보면 u라는 솔루션은 사실 $ A^{-1}\mathbf{b} $ 가 되어야한다. 그래서 $Au = b$라고 쓸 수 있다.
- 결국 어떤 다른 솔루션 u가 있다고 가정해도 모두 같다는 것을 알 수 있다.
Theorem6.
\[(A^{-1})^{-1} = A\]
a. If $A$ is an invertible matrix, then $A^{-1}$ is invertible andb. If $A$ and $B$ are $n \times n$ invertible matrices, then so is $AB$ , and the inverse of $AB$ is the product of the inverses of $A$ and $B$ in the reverse order. That is
\[(AB)^{-1} = B^{-1}A^{-1}\]c. If $A$ is an invertible matrix, then so is $A^T$ , and the inverse of $A^T$ is the transpose of $A^{-1}$ . that is,
\[(A^T)^{-1} = (A^{-1})^T\]
- a. $A$ 가 invertible matrix 이면 $A^{-1}$ 또한 invertible이다.
- b. 두 행렬의 곱의 역행렬은 순서가 바뀐 각각의 역행렬이다.
- c. $A$ 가 invertible 이면, $A^T$ 역시 invertible 이다.
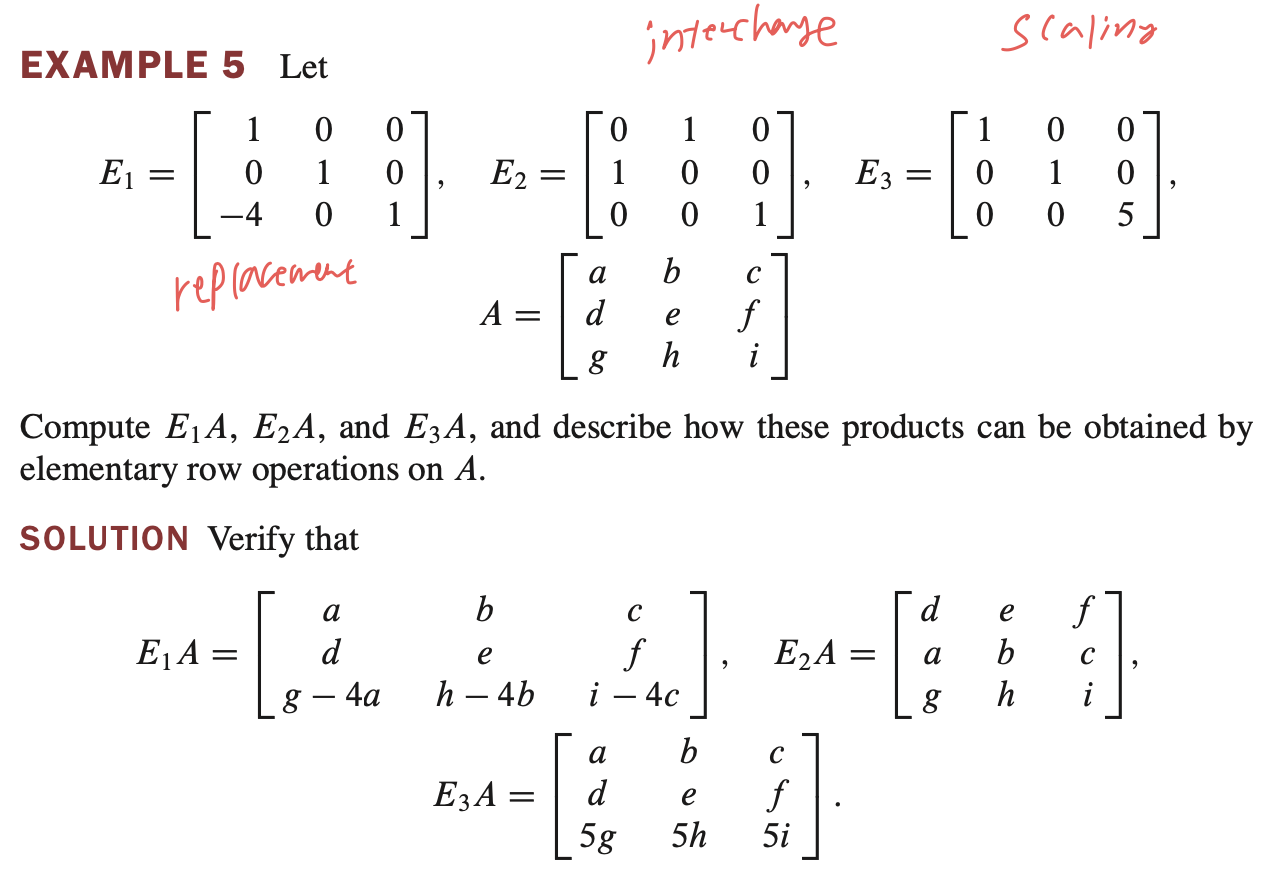
Elementary Matrices - 기본 행렬
elementary matrix(기본 행렬)는 identity matrix(항등 행렬)에 row operation 을 적용해서 얻을 수 있다.
이것을 가지고 알 수 있는 특성은 다음과 같다.
If an elementary row operation is performed on an $m \times n$ matrix $A$ , the resulting matrix can be written as $EA$ , where the $m \times m$ matrix $E$ is created by performing the same row operation on $I_m$ .
- $m \times n$ matrix 에 elementary row operation을 수행했다는 것은 어떤 $m \times m$ elementary matrix가 존재한다는 의미이다.
- $A$ 에 적용한 row operation을 $m \times m$ identity matrix에 적용하면 $E$ 가 생성된다.
Each elementary matrix $E$ is invertible. The inverse of $E$ is the elementary matrix of the same type that trnasforms $E$ back into $I$ .
- elementary matrix $E$ 가 invertible 이면 $E$ 의 inverse는 $E$ 를 $I$ 로 변환하는 elemenatry matrix 이다.
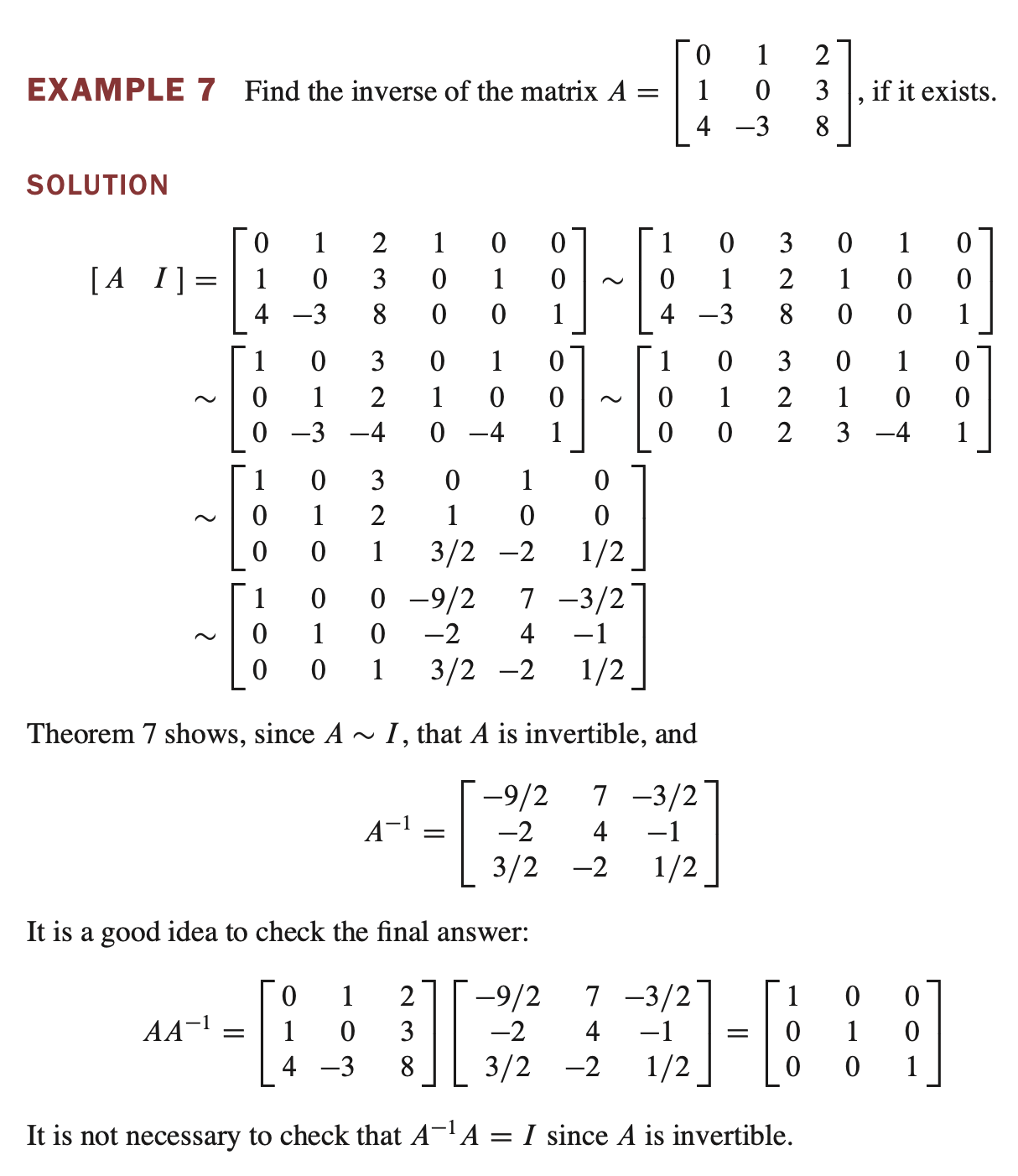
Theorem7.
An $n \times n$ matrix $A$ is invertible if and only if $A$ is row equivalent to $I_n$ , and in this case, any sequence of elementary row operations that reduces $A$ to $I_n$ also transforms $I_n$ into $A^{-1}$ .
- $A$ 가 $n \times n$ invertible matrix 이면 $A$ 는 $I_n$ 과 row equivalent 하다. $A$ 를 $I_n$ 으로 감소시키는 row operation 은 $I_n$을 $A^{-1}$ 로 변환한다.