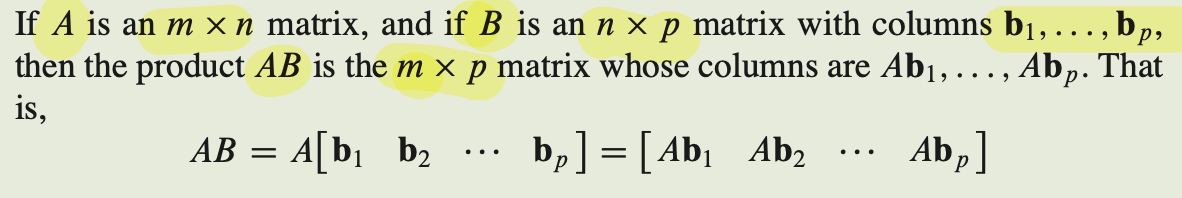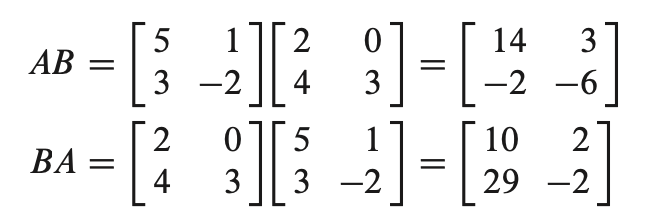Linear Algebra - 2.1 Matrix Operations
- Linear Algebra - 1.1 Systems of Linear Equations
- Linear Algebra - 1.2 Row Reduction and Echelon Forms
- Linear Algebra - 1.3 Vector Equations
- Linear Algebra - 1.4 The Matrix Equation Ax=b
- Linear Algebra - 1.5 Solution Sets of Linear Algebra
- Linear Algebra - 1.6 Linear Independence and Linear Dependence
- Linear Algebra - 1.7 Introduction to Linear Transformation
- Linear Algebra - 1.8 The Matrix of a Linear Transformation
- Linear Algebra - 2.1 Matrix Operations
- Linear Algebra - 2.2 The Inverse of Matrix
- Linear Algebra - 2.3 Characterizations of Invertible Matrices of
- Linear Algebra - 2.4 Partitioned Matrices
- Linear Algebra - 2.5 Matrix Factorizations, LU Decomposition
- Linear Algebra - 2.6 Subspaces of $\mathbb{R}^n$
- Linear Algebra - 2.7 Dimension and Rank
- Linear Algebra - 3.1 Introduction to Determinants
- Linear Algebra - 3.2 Properties of Determinants
- Linear Algebra - 3.3 Cramer's Rule, Volume, And Linear Transformations
- Linear Algebra - 4.1 Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues
- Linear Algebra - 4.2 The Characteristic Equation
- Linear Algebra - 4.3 Diagonalization
- Linear Algebra - 4.4 Eigenvectors And Linear Transformations
- Linear Algebra - 4.5 Complex Eigenvalues
- Linear Algebra - 5.1 Inner Product And Orthogonality
- Linear Algebra - 5.2 Orthogonal Sets
- Linear Algebra - 5.3 Orthogonal Projections
- Linear Algebra - 5.4 The Gram-Schmidt Process (그람 슈미츠 과정)
- Linear Algebra - 5.5 Least-Square Problems
- Linear Algebra - 6.1 Diagonalization of Symmetric Matrices
- Linear Algebra - 6.2 Quadratic Forms
- Linear Algebra - 6.3 Constrained Optimization
- Linear Algebra - 6.4 SVD, The Singular Value Decomposition
- Linear Algebra - 6.5 Reduced SVD, Pseudoinverse, Matrix Classification, Inverse Algorithm
용어 정리
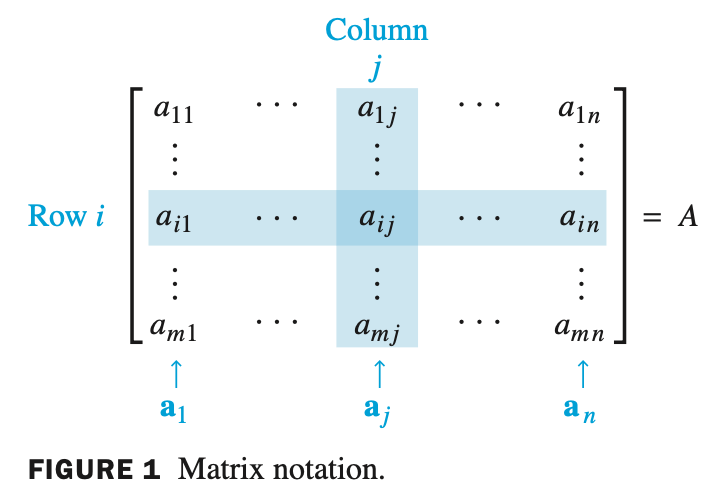
- Matrix Notation (행렬 표기법)
- Matrix Sum (행렬 덧셈)
- Scalar Multiple (선형 변환)
- Matrix Multiplication (행렬 곱)
- The transpose of a matrix (행렬의 전치)
Matrix Notation - 행렬 표기법
- $A$ 가 $m$ x $n$ 행렬이면 i 번째 행, j 번째 열에 있는 항목은 $a_{ij}$ 로 표기한다. 또한 $A$ 의 $(i,j)$ 항목이라고 부른다.
Theorem1.
Let $A, \, B, \,$ and $C$ be matrices of the same size, and let $r$ and $s$ be scalars.a. $A + B = B + A$ d. $r(A + B) = rA + rB$
b. $(A + B) + C = A + (B + C)$ e. $(r + s)A = rA + sA$
c. $A + 0 = A $ f. $r(sA) = (rs)A$
- Chapter 1 에서 공부했던 $\mathbb{R}^{n}$ space 에서 vector 의 성질과 동일하다.
- 각각의 matrix 는 column vector 로 이루어져 있다. 따라서 vector 의 성질을 만족하게 되어 theorem 1 을 만족하게 된다.
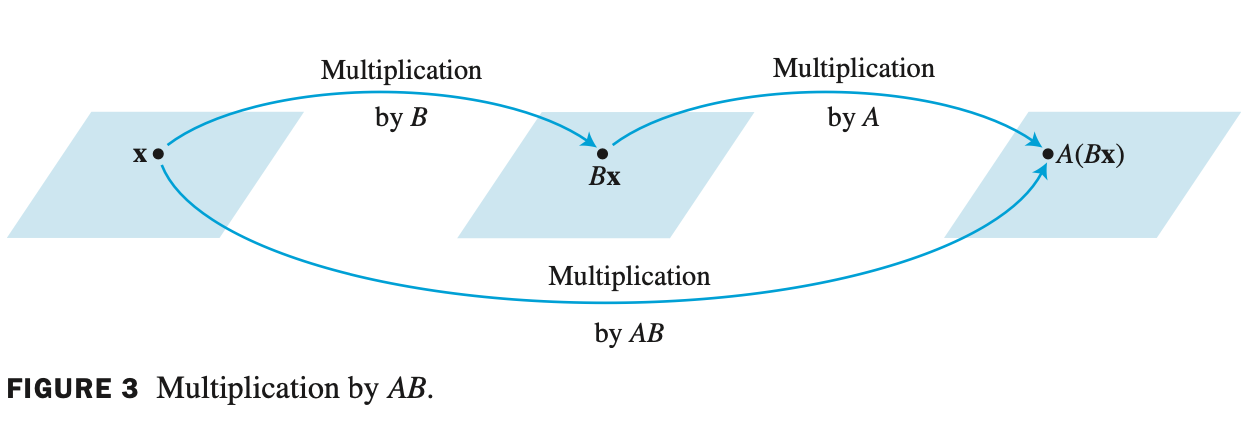
Matrix Multiplication - 행렬 곱
- Matrix Multiplication 과 Scalar Multiplication 은 다르다. Matrix Multiplication 에서는 matrix size 가 중요하다.
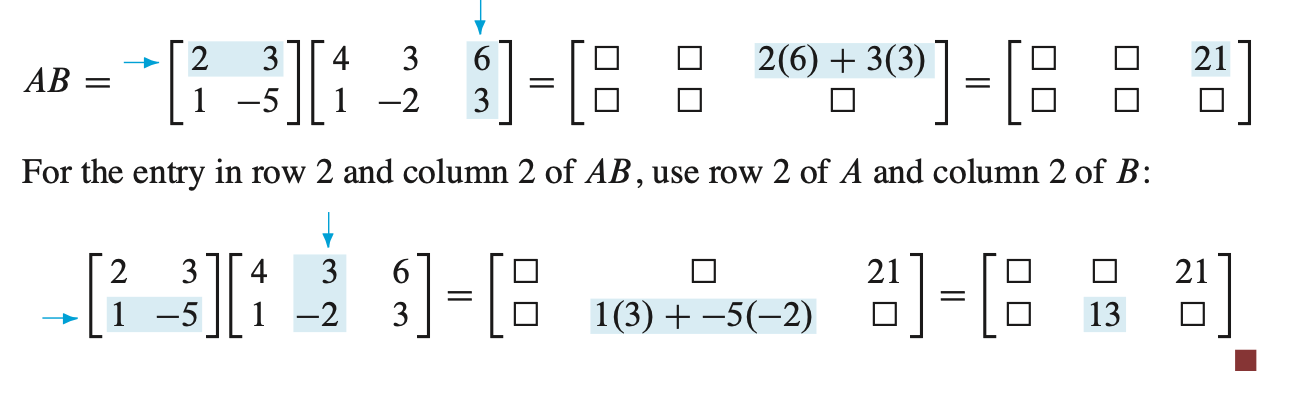
- $m$ x $n$ matrix A 와 $n$ x $p$ matrix B 를 곱하면 $m$ x $p$ matrix AB 를 생성한다.
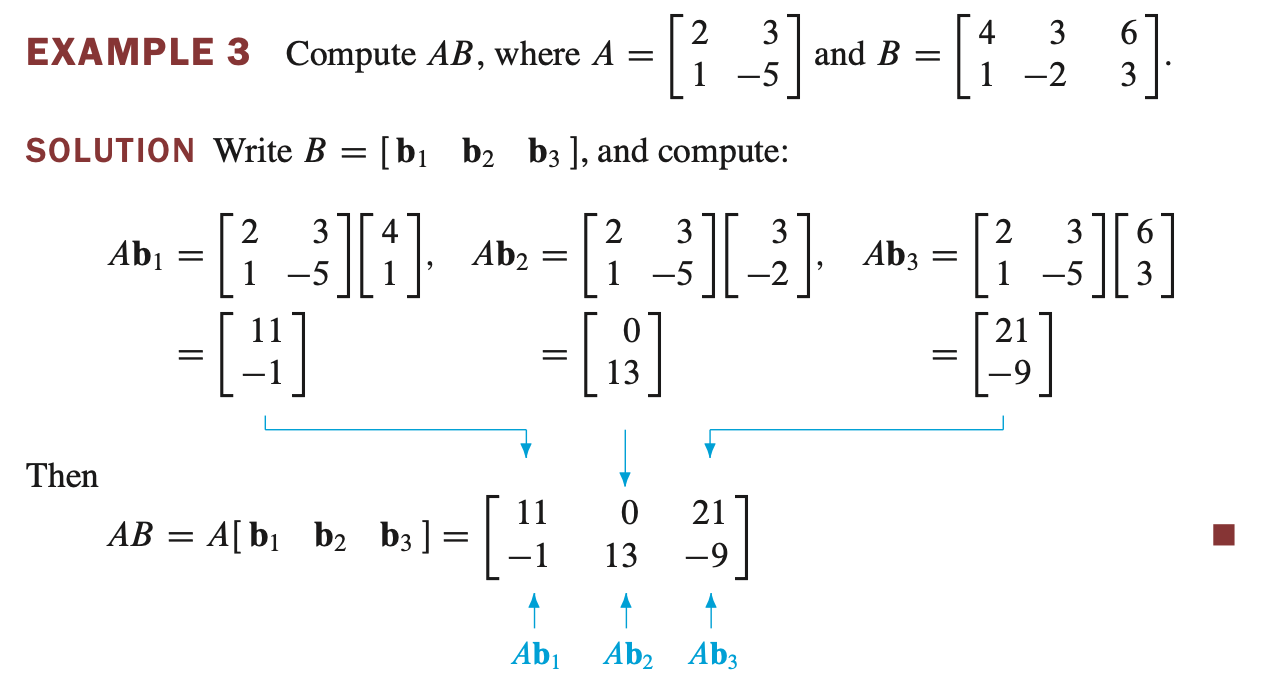
- AB 는 Ab1, Ab2, Ab3 를 나열한 matrix 이다.
행렬 곱셈은 내적을 통해서도 빠르게 연산이 가능하다.
Theorem2.
Let $A$ be an $m \times n$ matrix, and let $B$ and $C$ have sizes for which the indicated sums and products are defined.a. $A(BC) = (AB)C$
b. $A(B + C) = AB + BC$
c. $(B + C)A = BA + CA$
d. $r(AB) = (rA)B = A(rB)$ for any scalar $r$
e. $I_mA = A = AI_n$
- A, B, C 가 같은 size 를 갖고 있으면 위 성질을 만족한다. 주의! $AB \ne BA$
$\mathbf{WARNINGS:}$
$\mathbf{1.}$ In general, $AB \ne BA$.
$\mathbf{2.}$ The cancellation laws do not hold for matrix multiplication. That is, if $AB = AC$, then it is not true in general that $B = C$.
$\mathbf{3.}$ If a product $AB$ is the zero matrix, you cannot conclude in general that either $A = 0$ or $B = 0$.
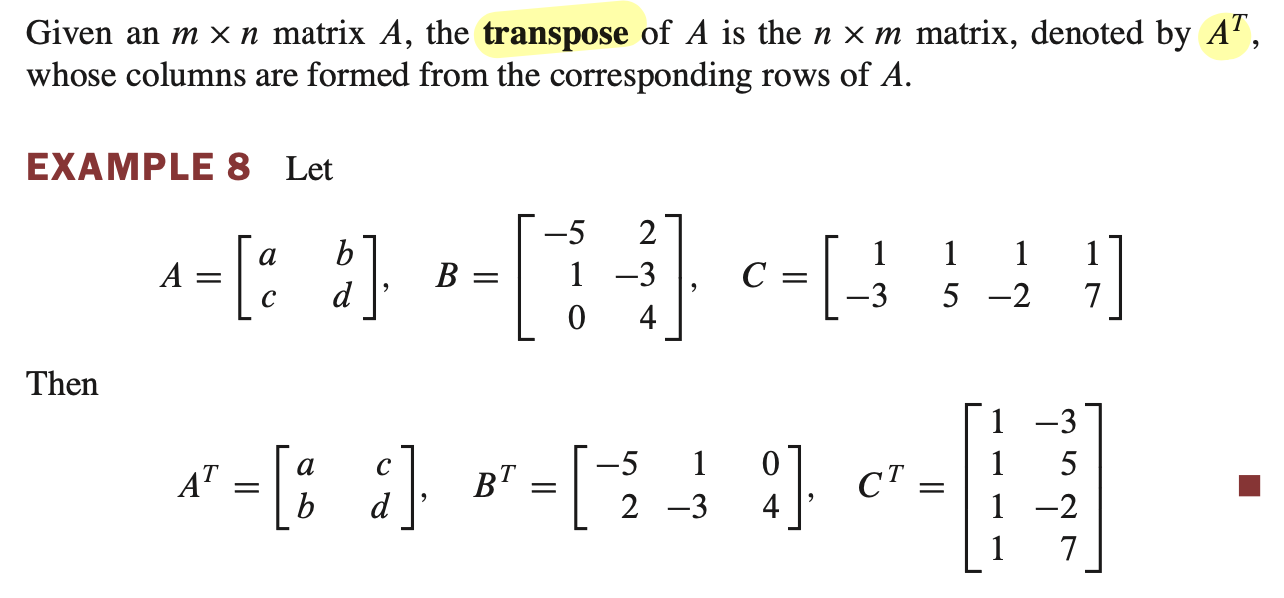
The Transpose of a Matrix - 행렬의 전치
Theorem3.
Let $A$ and $B$ denote matrices whose sizes are appropriate for the following sums and products.a. $(A^T)^T = A$
b. $(A + B)^T = A^T + B^T$
c. For any scalar $r$, $(rA)^T = rA^T$
d. $(AB)^T = B^TA^T$
- 성질 d 를 주의해야한다. transpose 를 하게 되면 matrix 의 size 가 변하므로.. 순서를 바꿔 size 를 동일하게 한다.